Spring Cloud - Hoxton.SR1(下)
13、Gateway新一代网关
13.1 概述简介
官网
上一代zuul 1.x:https://github.com/Netflix/zuul/wiki
当前gateway:https://cloud.spring.io/spring-cloud-static/spring-cloud-gateway/2.2.1.RELEASE/reference/html/
是什么
Cloud全家桶中有个很重要的组件就是网关,在1.x版本中都是采用的Zuul网关;
但在2.x版本中,zuul的升级一直跳票,SpringCloud最后自己研发了一个网关替代Zuul,那就是SpringCloud Gateway—句话:gateway是原zuul1.x版的替代
Gateway是在Spring生态系统之上构建的API网关服务,基于Spring 5,Spring Boot 2和Project Reactor等技术。
Gateway旨在提供一种简单而有效的方式来对API进行路由,以及提供一些强大的过滤器功能,例如:熔断、限流、重试等。
SpringCloud Gateway是Spring Cloud的一个全新项目,基于Spring 5.0+Spring Boot 2.0和Project Reactor等技术开发的网关,它旨在为微服务架构提供—种简单有效的统一的API路由管理方式。
SpringCloud Gateway作为Spring Cloud 生态系统中的网关,目标是替代Zuul,在Spring Cloud 2.0以上版本中,没有对新版本的Zul 2.0以上最新高性能版本进行集成,仍然还是使用的Zuul 1.x非Reactor模式的老版本。而为了提升网关的性能,SpringCloud Gateway是基于WebFlux框架实现的,而WebFlux框架底层则使用了高性能的Reactor模式通信框架Netty。
Spring Cloud Gateway的目标提供统一的路由方式且基于 Filter链的方式提供了网关基本的功能,例如:安全,监控/指标,和限流。
能干嘛?
- 反向代理
- 鉴权
- 流量控制
- 熔断
- 日志监控
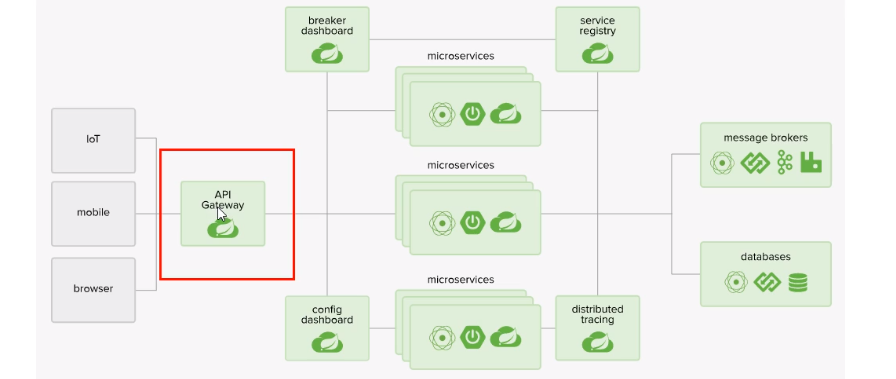
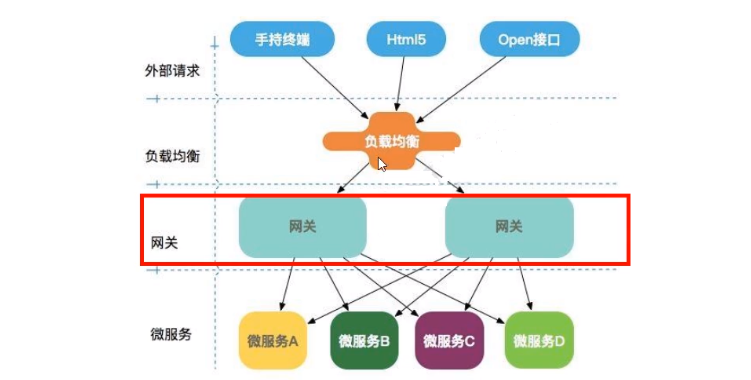
微服务架构中网关的位置
GateWay非阻塞异步模型
有Zuull了怎么又出来gateway
- netflix不太靠谱,zuul2.0一直跳票,迟迟不发布
- 一方面因为Zuul1.0已经进入了维护阶段,而且Gateway是SpringCloud团队研发的,是亲儿子产品,值得信赖。而且很多功能Zuul都没有用起来也非常的简单便捷
- Gateway是基于异步非阻塞模型上进行开发的,性能方面不需要担心。虽然Netflix早就发布了最新的Zuul 2.x,但Spring Cloud貌似没有整合计划。而且Netflix相关组件都宣布进入维护期;不知前景如何
- 多方面综合考虑Gateway是很理想的网关选择
- SpringCloud Gateway具有如下特性:
- 基于Spring Framework 5,Project Reactor和Spring Boot 2.0进行构建;
- 动态路由:能够匹配任何请求属性;
- 可以对路由指定Predicate (断言)和Filter(过滤器);
- 集成Hystrix的断路器功能;
- 集成Spring Cloud 服务发现功能;
- 易于编写的Predicate (断言)和Filter (过滤器);
- 请求限流功能;
- 支持路径重写。
- SpringCloud Gateway与Zuul的区别
- 在SpringCloud Finchley正式版之前,Spring Cloud推荐的网关是Netflix提供的Zuul;
- Zuul 1.x,是一个基于阻塞I/O的API Gateway;
- Zuul 1.x基于Servlet 2.5使用阻塞架构它不支持任何长连接(如WebSocket)Zuul的设计模式和Nginx较像,每次I/О操作都是从工作线程中选择一个执行,请求线程被阻塞到工作线程完成,但是差别是Nginx用C++实现,Zuul用Java实现,而JVM本身会有第-次加载较慢的情况,使得Zuul的性能相对较差;
- Zuul 2.x理念更先进,想基于Netty非阻塞和支持长连接,但SpringCloud目前还没有整合。Zuul .x的性能较Zuul 1.x有较大提升。在性能方面,根据官方提供的基准测试,Spring Cloud Gateway的RPS(每秒请求数)是Zuul的1.6倍;
- Spring Cloud Gateway建立在Spring Framework 5、Project Reactor和Spring Boot2之上,使用非阻塞API;
- Spring Cloud Gateway还支持WebSocket,并且与Spring紧密集成拥有更好的开发体验
Zuul1.x模型
Springcloud中所集成的Zuul版本,采用的是Tomcat容器,使用的是传统的Serviet IO处理模型。
Servlet的生命周期?servlet由servlet container进行生命周期管理。
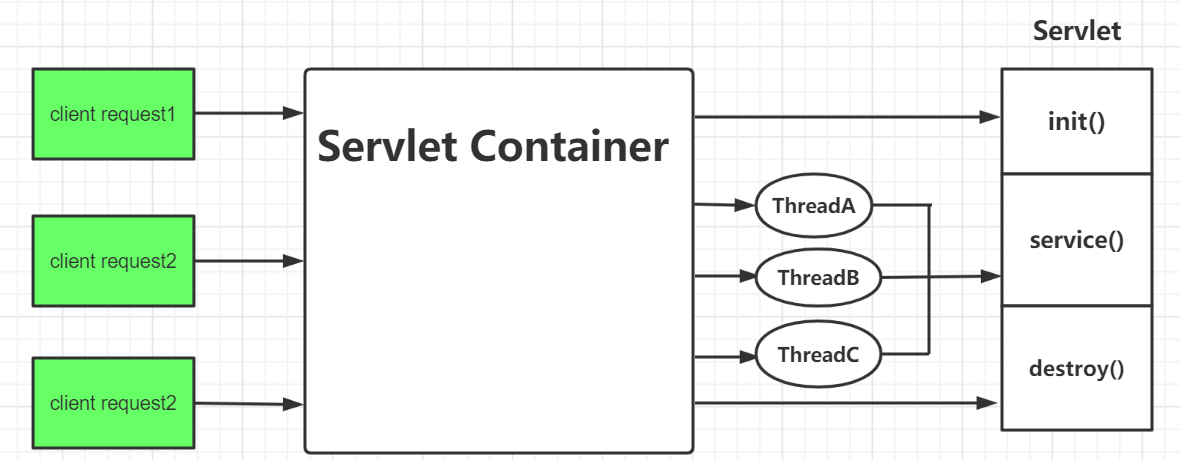
- container启动时构造servlet对象并调用servlet init()进行初始化;
- container运行时接受请求,并为每个请求分配一个线程(一般从线程池中获取空闲线程)然后调用service);
- container关闭时调用servlet destory()销毁servlet。
上述模式的缺点:
- Servlet是一个简单的网络IO模型,当请求进入Servlet container时,Servlet container就会为其绑定一个线程,在并发不高的场景下这种模型是适用的。但是一旦高并发(如抽风用Jmeter压),线程数量就会上涨,而线程资源代价是昂贵的(上线文切换,内存消耗大)严重影响请求的处理时间。在一些简单业务场景下,不希望为每个request分配一个线程,只需要1个或几个线程就能应对极大并发的请求,这种业务场景下servlet模型没有优势。
- 所以Zuul 1.X是基于servlet之上的一个阻塞式处理模型,即Spring实现了处理所有request请求的一个servlet (DispatcherServlet)并由该servlet阻塞式处理处理。所以SpringCloud Zuul无法摆脱servlet模型的弊端。
Gateway模型
- WebFlux是什么?官网:https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/spring-framework-reference/web-reactive.html#spring-webflux
- 传统的Web框架,比如说: Struts2,SpringMVC等都是基于Servlet APl与Servlet容器基础之上运行的。
- 但是在Servlet3.1之后有了异步非阻塞的支持。而WebFlux是一个典型非阻塞异步的框架,它的核心是基于Reactor的相关API实现的。相对于传统的web框架来说,它可以运行在诸如Netty,Undertow及支持Servlet3.1的容器上。非阻塞式+函数式编程(Spring 5必须让你使用Java 8)。
- Spring WebFlux是Spring 5.0 引入的新的响应式框架,区别于Spring MVC,它不需要依赖Servlet APl,它是完全异步非阻塞的,并且基于Reactor来实现响应式流规范。
13.2 三大核心概念
13.2.1 Route(路由)
路由是构建网关的基本模块,它由ID,目标URI,一系列的断言和过滤器组成,如断言为true则匹配该路由。
13.2.2 Predicate(断言)
参考的是Java8的java.util.function.Predicate,开发人员可以匹配HTTP请求中的所有内容(例如请求头或请求参数),如果请求与断言相匹配则进行路由。
13.2.3 Filter(过滤)
指的是Spring框架中GatewayFilter的实例,使用过滤器,可以在请求被路由前或者之后对请求进行修改。
13.2.4 总结
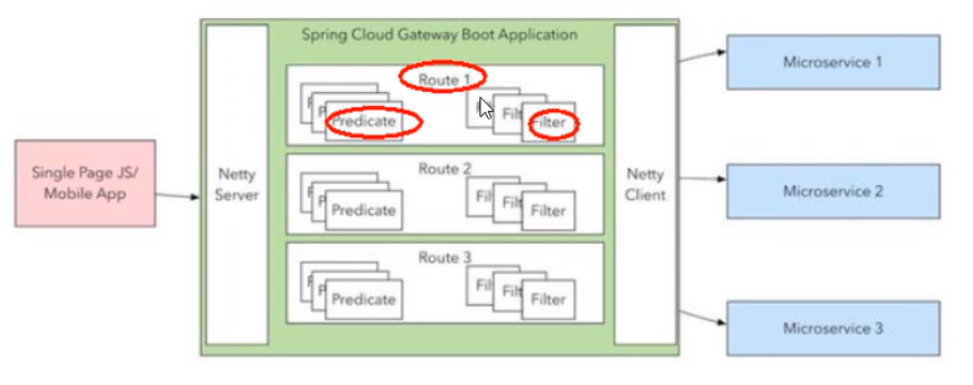
web请求,通过一些匹配条件,定位到真正的服务节点。并在这个转发过程的前后,进行一些精细化控制。
predicate就是我们的匹配条件;而fliter,就可以理解为一个无所不能的拦截器。有了这两个元素,再加上目标uri,就可以实现一个具体的路由了。
13.3 Gateway工作流程
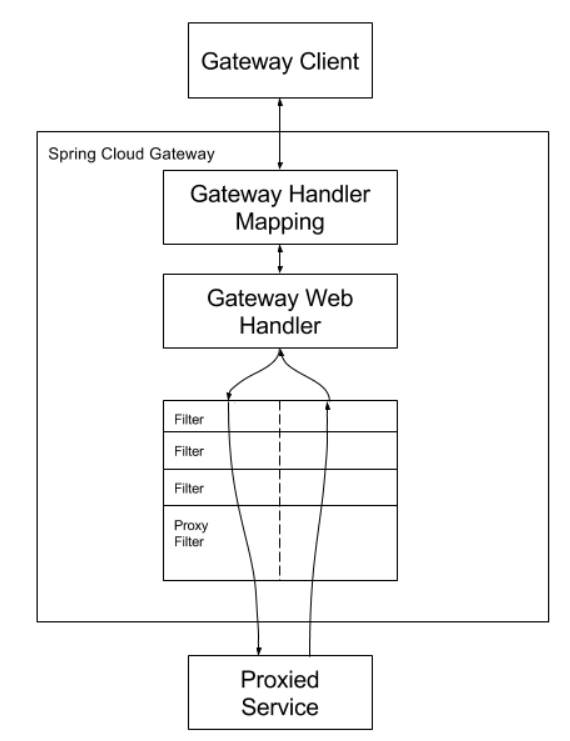
- 客户端向Spring Cloud Gateway发出请求。然后在Gateway Handler Mapping 中找到与请求相匹配的路由,将其发送到GatewayWeb Handler;
- Handler再通过指定的过滤器链来将请求发送到我们实际的服务执行业务逻辑,然后返回;
- 过滤器之间用虚线分开是因为过滤器可能会在发送代理请求之前(“pre”)或之后(“post")执行业务逻辑;
- Filter在“pre”类型的过滤器可以做参数校验、权限校验、流量监控、日志输出、协议转换等,在“post”类型的过滤器中可以做响应内容、响应头的修改,日志的输出,流量监控等有着非常重要的作用。
核心逻辑:路由转发 + 执行过滤器链。
13.4 入门配置
13.4.1 Gateway9527搭建
新建Module:cloud-gateway-gateway9527
POM
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>springcloud2020</artifactId>
<groupId>com.gyz.clouddemo</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>cloud-gateway-gateway9527</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<!--gateway-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--eureka-client-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 引入自己定义的api通用包,可以使用Payment支付Entity -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.gyz.clouddemo</groupId>
<artifactId>cloud-api-commons</artifactId>
<version>${project.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!--一般基础配置类-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
YML
server:
port: 9527
spring:
application:
name: cloud-gateway
eureka:
client: #服务提供者provider注册进eureka服务列表内
service-url:
register-with-eureka: true
fetch-registry: true #是否去注册中心获取其他服务的地址
defaultZone: http://eureka7001:com:7001/eureka
instance:
hostname: cloud-gateway-service
主启动类
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
public class GateWayMain9527 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(GateWayMain9527.class, args);
}
}
9527网关如何做路由映射?
- 看看
cloud-provider-payment8001的controller的访问地址:- get
- lb
- 我们目前不想暴露8001端口,希望在8001外面套一层9527
YML新增网关配置
server:
port: 9527
spring:
application:
name: cloud-gateway
cloud: ##############新增网关配置##################
gateway:
routes:
- id: payment_routh #路由的ID,没有固定规则但要求唯一,建议配合服务名
uri: http://localhost:8001 #匹配后提供服务的路由地址
predicates:
- Path=/payment/get/** # 断言,路径相匹配的进行路由
- id: payment_routh2
uri: http://localhost:8001
predicates:
- Path=/payment/lb/** # 断言,路径相匹配的进行路由
eureka:
client: #服务提供者provider注册进eureka服务列表内
service-url:
register-with-eureka: true
fetch-registry: true
defaultZone: http://eureka7001:com:7001/eureka
instance:
hostname: cloud-gateway-service
测试
- 启动
cloud-eureka-server7001 - 启动
cloud-provider-payment8001 - 启动
cloud-gateway-gateway9527 - 访问均可成功:
Gateway网关路由有两种配置方式:
在配置文件yml中配置
代码中注入RouteLocator的Bean
RemoteAddressResolver resolver = XForwardedRemoteAddressResolver .maxTrustedIndex(1); ... .route("direct-route", r -> r.remoteAddr("10.1.1.1", "10.10.1.1/24") .uri("https://downstream1") .route("proxied-route", r -> r.remoteAddr(resolver, "10.10.1.1", "10.10.1.1/24") .uri("https://downstream2") )业务需求:通过9527网关访问到外网的百度新闻网址(https://news.baidu.com/guonei)
编码:
/** * @Description 通过9527网关访问到外网的百度新闻网址(https://news.baidu.com/guonei) * @Author GongYuZhuo * @Date 2021/7/25 15:48 * @Version 1.0.0 */ @Configuration public class GateWayConfig { @Bean public RouteLocator cutstomRouteLocator(RouteLocatorBuilder locatorBuilder) { RouteLocatorBuilder.Builder routes = locatorBuilder.routes(); routes.route("gateway-service-gyz", r -> r.path("/guonei").uri("https://news.baidu.com/guonei")).build(); return routes.build(); } }
13.5 通过服务名实现动态
默认情况下Gatway会根据注册中心注册的服务列表, 以注册中心上微服务名为路径创建动态路由进行转发,从而实现动态路由的功能。
启动:一个eureka7001+两个服务提供者8001/8002
这三个服务的POM都需加上:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
YML:
- 需要注意的是uri的协议lb,表示启用Gateway的负载均衡功能
lb://serverName是spring cloud gatway在微服务中自动为我们创建的负载均衡uri
server:
port: 9527
spring:
application:
name: cloud-gateway
cloud: ##############新增网关配置##################
gateway:
routes:
- id: payment_routh #路由的ID,没有固定规则但要求唯一,建议配合服务名
#uri: http://localhost:8001 #匹配后提供服务的路由地址
uri: lb://cloud-payment-service #匹配后提供服务的路由地址
predicates:
- Path=/payment/get/** # 断言,路径相匹配的进行路由
- id: payment_routh2
#uri: http://localhost:8001
uri: lb://cloud-payment-service #匹配后提供服务的路由地址
predicates:
- Path=/payment/lb/** # 断言,路径相匹配的进行路由
discovery:
locator:
enabled: true #开启从注册中心动态创建路由的功能,利用微服务名进行路由
eureka:
client: #服务提供者provider注册进eureka服务列表内
service-url:
register-with-eureka: true
fetch-registry: true
defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka
instance:
hostname: cloud-gateway-service
测试:
- 浏览器输入:http://localhost:9527/payment/lb
- 8001和8002两个端口来回切换
13.6 GateWay常用的Predicate
13.6.1 Predicate是什么
启动cloud-gateway-gateway9527会包含如下信息:

13.6.2 Route Predicate Factories这个是什么
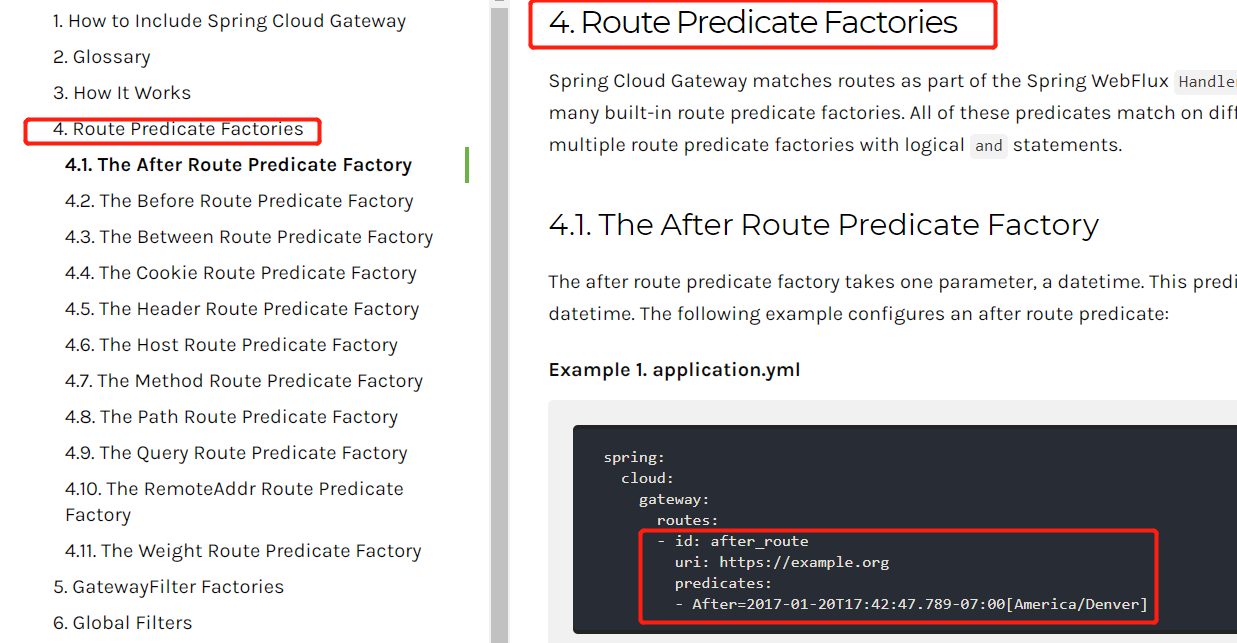
- Spring Cloud Gateway将路由匹配作为Spring WebFlux HandlerMapping基础架构的一部分
- Spring Cloud Gateway包括许多内置的Route Predicate工厂。所有这些Predicate都与HTTP请求的不同属性匹配。多RoutePredicate工厂可以进行组合
- Spring Cloud Gateway创建Route 对象时,使用RoutePredicateFactory 创建 Predicate对象,Predicate 对象可以赋值给Route。Spring Cloud Gateway包含许多内置的
Route Predicate Factories - 所有这些谓词都匹配HTTP请求的不同属性。多种谓词工厂可以组合,并通过逻辑and
13.6.3 常用的Route Predicate
The After Route Predicate Factory
The Before Route Predicate Factory
The Between Route Predicate Factory
The Cookie Route Predicate Factory
The Header Route Predicate Factory
The Host Route Predicate Factory
The Method Route Predicate Factory
The Path Route Predicate Factory
The Query Route Predicate Factory
The RemoteAddr Route Predicate Factory
The Weight Route Predicate Factory
The After Route Predicate Factory
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: after_route
uri: https://example.org
predicates:
# 这个时间后才能起效
- After=2017-01-20T17:42:47.789-07:00[America/Denver]
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
public class ZonedDateTimeDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ZonedDateTime zbj = ZonedDateTime.now(); // 默认时区
System.out.println(zbj);
}
}
The Cookie Route Predicate Factory
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: cookie_route
uri: https://example.org
predicates:
- Cookie=chocolate, ch.p
Cookie Route Predicate 需要两个参数,一个时Cookie name,一个是正则表达式。
路由规则会通过获取对应的Cookie name值和正则表达式去匹配,如果匹配上就会执行路由,如果没有匹配上就不执行
Curl命令可以通过命令行的方式,执行Http请求,这在我们开发时很有用,我们可以使用它来模拟一些http客户端请求。
The Host Route Predicate Factory
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: host_route
uri: https://example.org
predicates:
- Host=**.somehost.org,**.anotherhost.org
Host Route Predicate接收一组参数,一组匹配的域名列表,这个模板是ant 分隔的模板,用. 号作为分隔符,它通过参数中的主机地址作为匹配规则。
The Query Route Predicate Factory
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: query_route
uri: https://example.org
predicates:
- Query=green
支持传入两个参数,一个是属性名、一个是属性值,属性值可以是正则表达式。
总结
- 说白了,Predicate就是为了实现一组匹配规则, 让请求过来找到对应的Route进行处理

13.7 GateWay的Filter
13.7.1 概述
- 路由过滤器可用于修改进入的HTTP请求和返回的HTTP响应,路由过滤器只能指定路由进行使用;
- Spring Cloud Gateway内置了多种路由过滤器,他们都由GatewayFilter的工厂类来产生。
13.7.2 Spring Cloud Gateway的filter
生命周期:
- pre
- post
种类:
- GatewayFilter:https://cloud.spring.io/spring-cloud-static/spring-cloud-gateway/2.2.1.RELEASE/reference/html/#gatewayfilter-factories
- GlobalFilter:https://cloud.spring.io/spring-cloud-static/spring-cloud-gateway/2.2.1.RELEASE/reference/html/#global-filters
13.7.3 常用的GatewayFilter
AddRequestParameter
YML:
server: port: 9527 spring: application: name: cloud-gateway cloud: ##############新增网关配置################## gateway: routes: - id: payment_routh #路由的ID,没有固定规则但要求唯一,建议配合服务名 #uri: http://localhost:8001 #匹配后提供服务的路由地址 uri: lb://cloud-payment-service #匹配后提供服务的路由地址 predicates: - Path=/payment/get/** # 断言,路径相匹配的进行路由 filters: - AddRequestParameter=X-Request-Id,1024 #过滤工厂会在匹配的请求头上加一对请求头,名称为X-Request-Id 值为1024 - id: payment_routh2 #uri: http://localhost:8001 uri: lb://cloud-payment-service #匹配后提供服务的路由地址 predicates: - Path=/payment/lb/** # 断言,路径相匹配的进行路由 discovery: locator: enabled: true #开启从注册中心动态创建路由的功能,利用微服务名进行路由 eureka: client: #服务提供者provider注册进eureka服务列表内 service-url: register-with-eureka: true fetch-registry: true defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka instance: hostname: cloud-gateway-service
13.7.4 自定义全局GlobalFilter
两个主要接口介绍:implments GlobalFilter,Ordered
作用:
- 全局日志记录
- 统一网关鉴权
在cloud-gateway-gateway9527新增Filter类,案例代码:
/**
* @Description 自定义全局过滤器
* @Author GongYuZhuo
* @Date 2021/7/25 17:06
* @Version 1.0.0
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class MyLogGatewayFilter implements GlobalFilter, Ordered {
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) {
log.info("***********come in MyLogGateWayFilter: " + new Date());
String uname = exchange.getRequest().getQueryParams().getFirst("uname");
if (uname == null) {
log.info("*******用户名为null,非法用户,o(╥﹏╥)o");
exchange.getResponse().setStatusCode(HttpStatus.NOT_ACCEPTABLE);
return exchange.getResponse().setComplete();
}
return chain.filter(exchange);
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return 0;
}
}
测试:
启动顺序:7001、8001、9527、8002
浏览器输入:
14、Spring Cloud config分布式配置中心
14.1 概述
14.1.1 分布式系统面临的问题--配置问题
微服务意味着要将单体应用中的业务拆分成一个个子服务,每个服务的粒度相对较小,因此系统中会出现大量的服务。由于每个服务都需要必要的配置信息才能运行,所以一套集中式的、动态的配置管理设施是必不可少的。
SpringCloud提供了ConfigServer【配置中心】来解决这个问题,我们每一个微服务自己都带着一个
application.yml,上百个配置文件的管理就要管理上百个application.yml
14.1.2 配置中心是什么
官网: https://cloud.spring.io/spring-cloud-static/spring-cloud-config/2.2.1.RELEASE/reference/html/
SpringCloud Config为微服务架构中的微服务提供集中化的外部配置支持,配置服务器为各个不同微服务应用的所有环境提供了一个中心化的外部配置;
14.1.3 配置中心怎么用
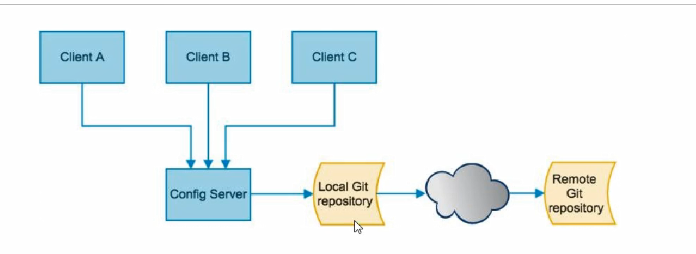
SpringCloud Config分为服务端和客户端两部分:
- 服务端也称为分布式配置中心,它是一个独立的微服务应用,用来连接配置服务器并为客户端提供获取配置信息,加密/解密信息等访问接口;
- 客户端则是通过指定的配置中心来管理应用资源,以及与业务相关的配置内容,并在启动的时候从配置中心获取和加载配置信息配置服务器默认采用git来存储配置信息,这样就有助于对环境配置进行版本管理,并且可以通过git客户端工具来方便的管理和访问配置内容。
14.1.4 配置中心作用
- 集中管理配置文件
- 不同环境不同配置,动态化的配置更新,分环境部署比如dev/test/prod/beta/release
- 运行期间动态调整配置,不再需要在每个服务部署的机器上编写配置文件,服务会向配置中心统一拉取配置自己的信息
- 当配置发生变动时,服务不需要重启即可感知到配置的变化并应用新的配置
- 将配置信息以REST接口的形式暴露 - post/crul访问刷新即可
14.1.5 与GitHub整合配置
由于SpringCloud Config默认使用Git来存储配置文件(也有其它方式,比如支持SVN和本地文件),但最推荐的还是Git,而且使用的是http/https访问的形式。
官网:https://cloud.spring.io/spring-cloud-static/spring-cloud-config/2.2.1.RELEASE/reference/html/
14.2 Config服务端配置与测试
14.2.1 操作步骤
用自己的账号在GitHub上新建一个名为
springcloud-config的新Repository。新建仓库的git地址 : git@github.com:xxx/springcloud-config.git
本地硬盘目录上新建Git仓库并clone上述地址仓库,会创建springcloud-config的文件夹
在springcloud-config的文件夹下创建三个yml文件
config-dev.yml
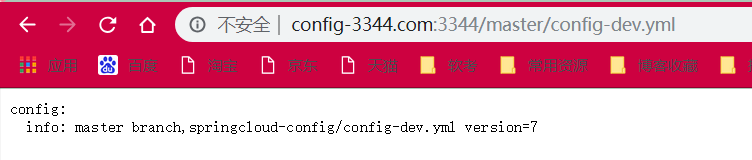
config: info: "master branch,springcloud-config/config-dev.yml version=7"config-prod.yml
config: info: "master branch,springcloud-config/config-prod.yml version=1"config-test.yml
config: info: "master branch,springcloud-config/config-test.yml version=1"推送到仓库
git add . git commit -m "描述推送内容" git push origin master
新建Module模块
cloud-config-center-3344,它即为Cloud的配置中心模块CloudConfig Centerpom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <parent> <artifactId>springcloud2020</artifactId> <groupId>com.gyz.clouddemo</groupId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> </parent> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <artifactId>cloud-config-center-3344</artifactId> <dependencies> <!-- 分布式配置中心 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-config-server</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.gyz.clouddemo</groupId> <artifactId>cloud-api-commons</artifactId> <version>${project.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>YML
server: port: 3344 spring: application: name: cloud-config-center #注册进Eureka服务器的微服务名 cloud: config: server: git: uri: git@github.com:xxx/springcloud-config.git #GitHub上面的git仓库名字 ####搜索目录 search-paths: - springcloud-config ####读取分支 label: master #服务注册到eureka地址 eureka: client: service-url: defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka主启动类
@EnableConfigServer/** * @Description @EnableConfigServer 激活配置中心 * @Author GongYuZhuo * @Date 2021/7/25 18:20 * @Version 1.0.0 */ @SpringBootApplication @EnableConfigServer public class ConfigCenterMain3344 { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ConfigCenterMain3344.class,args); } }windows下修改hosts文件(位置:C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\HOSTS),增加映射
127.0.0.1 config-3344.com测试通过Config微服务是否可以从GitHub上获取配置内容
启动微服务3344
页面返回结果:
14.2.2 配置读取规则
/{label}/{application}-{profile}.yml(推荐)
- 读取master分支
- 读取dev分支
/{application}-{profile}.yml
- http://config-3344.com:3344/config-dev.yml
- http://config-3344.com:3344/config-test.yml
- http://config-3344.com:3344/config-prod.yml
- http://config-3344.com:3344/config-xxxx.yml(不存在的配置)
/{application}/{profile}[/{label}]
- http://config-3344.com:3344/config/dev/master
- http://config-3344.com:3344/config/test/master
- http://config-3344.com:3344/config/test/dev
总结
- label:分支(branch)
- name:服务名
- profiles:环境(dev/test/prod)
14.3 Config客户端配置与测试
新建cloud-config-center-3355
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>springcloud2020</artifactId>
<groupId>com.gyz.clouddemo</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>cloud-config-center-3355</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
bootstrap.yml
applicaiton.yml是用户级的资源配置项
bootstrap.yml是系统级的,优先级更加高
Spring Cloud会创建一个Bootstrap Context,作为Spring应用的Application Context的父上下文
初始化的时候,BootstrapContext负责从外部源加载配置属性并解析配置。这两个上下文共享一个从外部获取的Environment
Bootstrap属性有高优先级,默认情况下,它们不会被本地配置覆盖。Bootstrap context和Application Context有着不同的约定,所以新增了一个bootstrap.yml文件,保证Bootstrap Context和Application Context配置的分离
要将Client模块下的application.yml文件改为bootstrap.yml,这是很关键的,因为bootstrap.yml是比application.yml先加载的。bootstrap.yml优先级高于application.yml。
配置内容:
server: port: 3355 spring: application: name: config-client cloud: #Config客户端配置 config: label: master #分支名称 name: config #配置文件名称 profile: dev #读取后缀名称 上述3个综合:master分支上config-dev.yml的配置文件被读取http://config-3344.com:3344/master/config-dev.yml uri: http://localhost:3344 #配置中心地址k #服务注册到eureka地址 eureka: client: service-url: defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka
修改config-dev.yml配置并提交到GitHub中,比如加个变量age或者版本号version
主启动
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
public class ConfigClientMain3355 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ConfigClientMain3355.class, args);
}
}
业务类
@Value("${config.info}")是从github上的配置文件中获取到的
@RestController
public class ConfigClientController {
/** 这里取的值是从github上取回来的*/
@Value("${config.info}")
private String configInfo;
@RequestMapping("/test/config/info")
public String test() {
return configInfo;
}
}
测试
- 启动Config配置中心3344微服务并自测
- 启动3355作为Client准备访问
- 成功实现了客户端3355访问SpringCloud Config3344通过GitHub获取配置信息,问题随之而来,分布式配置的动态刷新问题
- Linux运维修改GitHub上的配置文件内容做调整
- 刷新3344,发现ConfigServer配置中心立刻响应
- 刷新3355,发现ConfigClient客户端没有任何响应
- 3355没有变化除非自己重启或者重新加载
- 难到每次运维修改配置文件,客户端都需要重启??噩梦
14.4 Config客户端只动态刷新
避免每次更新配置都要重启客户端微服务3355
14.4.1 动态刷新
修改3355模块:
POM引入actuator监控
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId> </dependency>修改YML,暴露监控接口
# 暴露监控端点 management: endpoints: web: exposure: include: "*"@RefreshScope业务类Controller修改
@RestController @RefreshScope //使配置文件中的配置修改后不用重启项目即生效 public class ConfigClientController { ... }测试
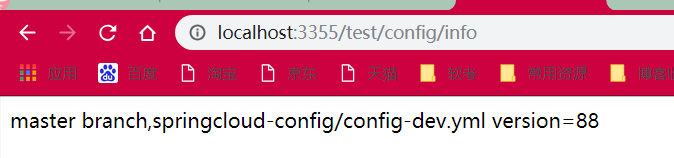
此时修改github配置文件内容 -> 访问3344(http://config-3344.com:3344/master/config-dev.yml) -> 访问3355(http://localhost:3355/test/config/info)
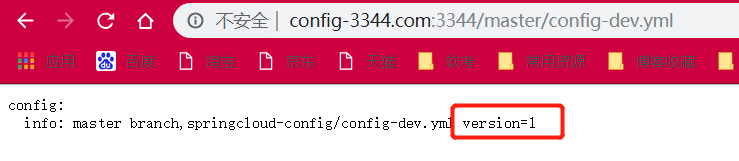
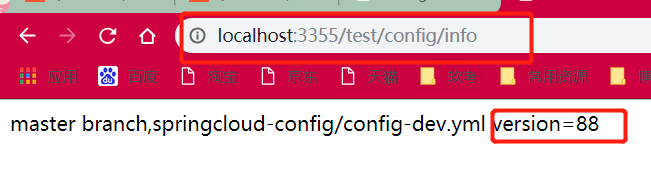
3355还是没有改变,还需一步:需要运维人员通过
cmd窗口发送Post请求刷新3355curl -X POST "http://localhost:3355/actuator/refresh"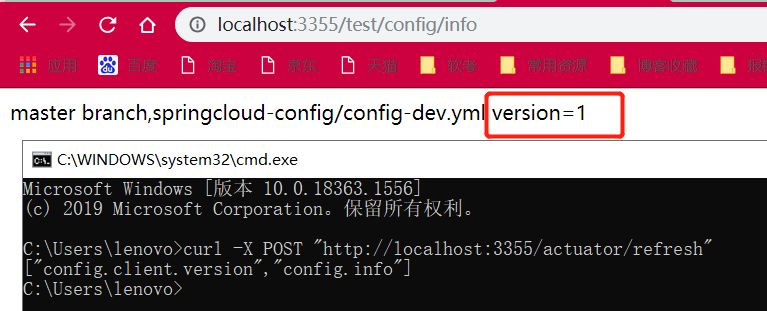
成功实现了客户端3355刷新到最新配置内容,避免了服务重启
想想还有什么问题?
- 假如有多个微服务客户端3355/3366/3377
- 每个微服务都要执行—次post请求,手动刷新?
- 可否广播,一次通知,处处生效?
- 我们想大范围的自动刷新,所以这就需要使用消息总线来进行广播。
15、Spring Cloud Bus消息总线
15.1 概述
SpringCloud Bus配合Springcloud Config使用可以实现配置的动态刷新。
15.1.1 是什么
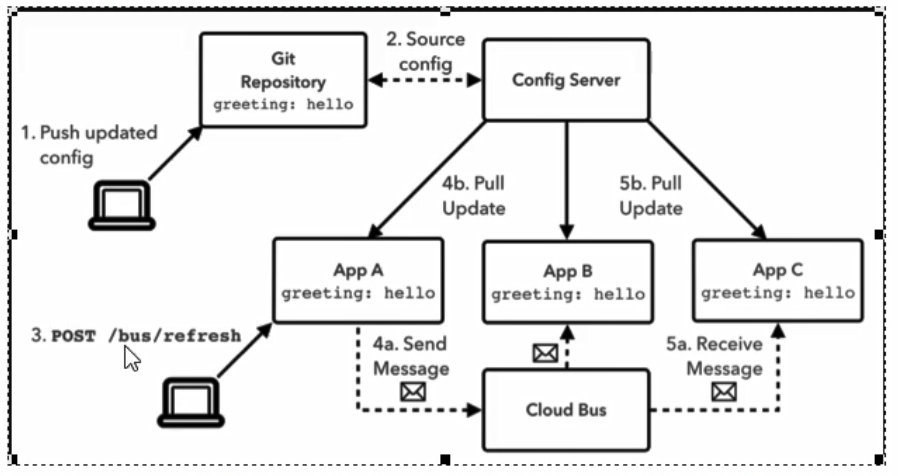
- Spring Cloud Bus是用来将分布式系统的节点与轻量级消息系统链接起来的框架,它整合了Java的事件处理机制和消息中间件的功能。
- Spring Clud Bus目前支持
RabbitMQ和Kafka。
15.1.2 能干嘛
Spring Cloud Bus能管理和传播分布式系统间的消息,就像一个分布式执行器,可用于广播状态更改、事件推送等,也可以当作微服务间的通信通道。
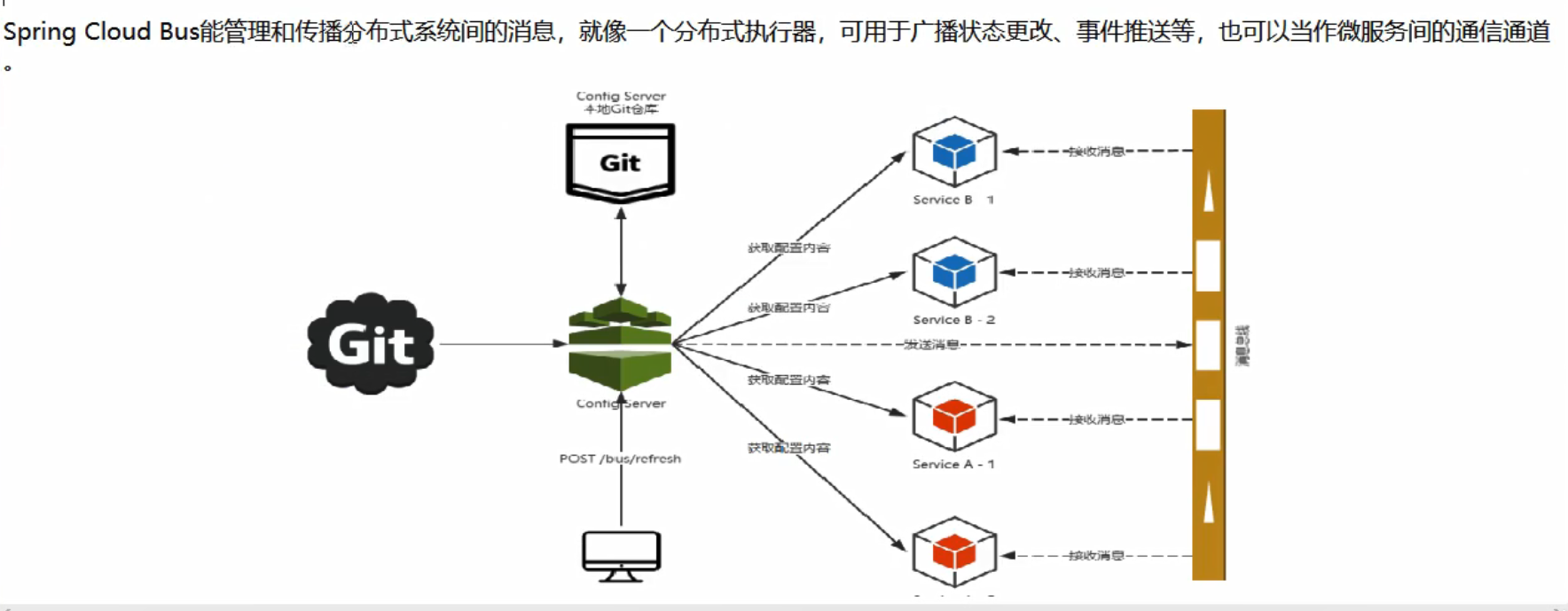
15.1.3 为何被称为总线
什么是总线?
在微服务架构的系统中,通常会使用轻量级的消息代理来构建一个公用的消息主题,并让系统中的所有微服务实例都连接上来。由于该主题中产生的消息会被所有实例监听和消费,所以称为消息总线。在总线上的各个实例,都可以方便地广播一些需要让其他链接在该主题行的实例都知道的消息。
基本原理:
ConfigClient实例都监听MQ中的同一个topic(默认是SpringcloudBus)。当一个服务刷新数据的时候,它会把这个信息放入到topic中,这样其它监听同一个topic的服务就能得到通知,然后去更新自身的配置。
15.2 RabbitMQ环境配置
安装Erlang,下载地址:http://erlang.org/download/otp_win64_21.3.exe
安装RabbitMQ,下载地址:https://github.com/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-server/releases/download/v3.8.3/rabbitmq-server-3.8.3.exe
进入RabbitMQ安装目录下的sbin目录,在位置栏输入cmd打开命令窗口,输入以下命令启动管理功能:
rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management
这样就可以添加可视化插件:
- 访问地址查看是否安装成功:http://localhost:15672/
- 输入账号密码并登录:guest guest
15.3 SpringCloud Bus动态刷新全局广播
15.3.1 必须先具备良好的RabbitMQ环境;
15.3.2 演示广播效果增加复杂度,再以3355为模板制作一个3366:
新建
cloud-config-client-3366POM文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <parent> <artifactId>springcloud2020</artifactId> <groupId>com.gyz.clouddemo</groupId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> </parent> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <artifactId>cloud-config-client-3366</artifactId> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>YML
server: port: 3366 spring: application: name: config-client cloud: config: label: master #分支名称 name: config #配置文件名称 profile: dev #读取后缀名称 上述三个综合http://localhost:3344/master/config-dev.yml uri: http://localhost:3344 #配置中心的地址 eureka: client: service-url: defaultZone: http://www.eureka7001.com:7001/eureka/ management: endpoints: web: exposure: include: "*"主启动
@SpringBootApplication @EnableEurekaClient public class ConfigClientMain3366 { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ConfigClientMain3366.class,args); } }controller
@RestController @Slf4j public class ConfigClientController { @Value("${server.port}") private String serverPort; @Value("${config.info}") private String configInfo; @GetMapping("/configInfo") public String configInfo() { return "serverPort: " + serverPort + "\t\n\n configInfo: " + configInfo; } }
设计思想
- 利用消息总线触发一个客户端/bus/refresh,而刷新所有客户端的配置
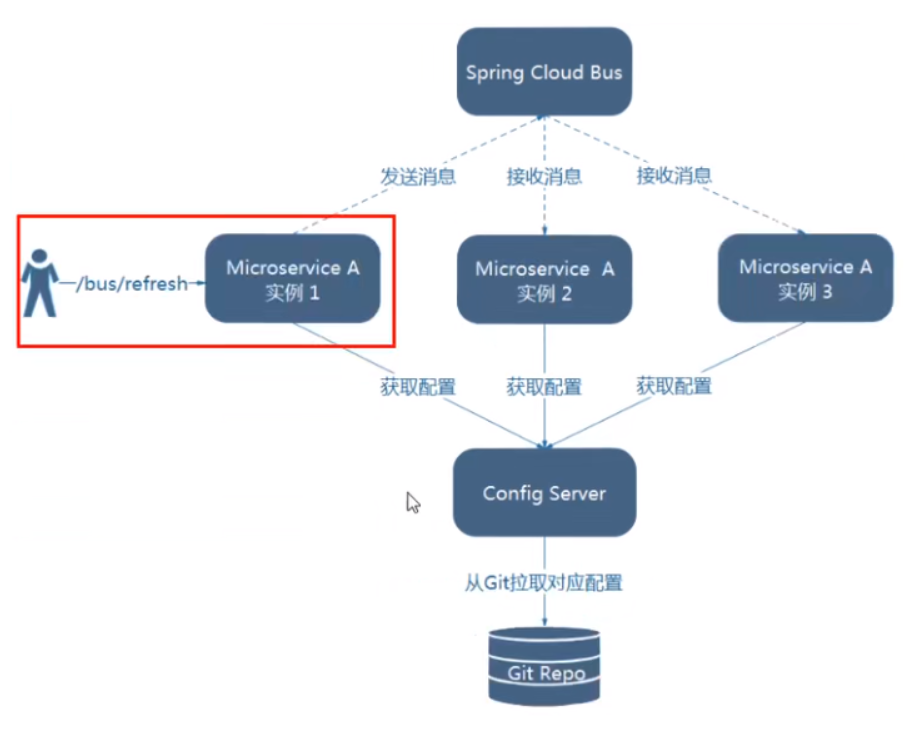
- 利用消息总线触发一个服务端ConfigServer的/bus/refresh端点,而刷新所有客户端的配置
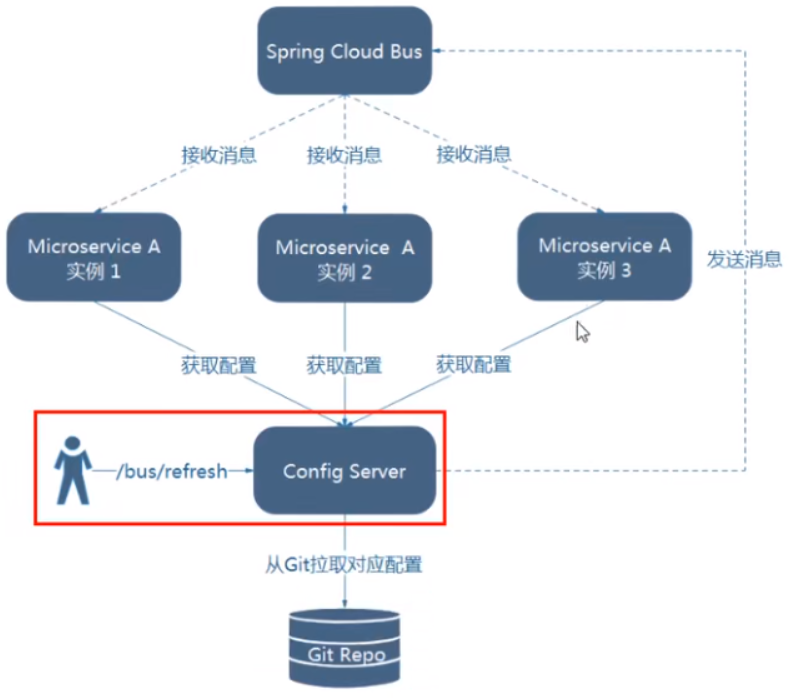
图二的架构显然更加合适,图一不适合的原因如下:
- 打破了微服务的职责单一性,因为微服务本身是业务模块,它不应该承担配置刷新的职责
- 打破了微服务各个节点的对等性
- 有一定的局限性。例如:微服务在迁移时,它的网络地址常常会发生变化,此时如果想要做到自动刷新,那就回增加更多的的修改
15.3.3 配置实现
给cloud-config-center-3344配置中心服务端添加消息总线支持
POM新增
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-bus-amqp</artifactId> </dependency>YML
server: port: 3344 spring: application: name: cloud-config-center #注册进Eureka服务器的微服务名 cloud: config: server: git: uri: git@github.com:xxx/springcloud-config.git #GitHub上面的git仓库名字 ####搜索目录 search-paths: - springcloud-config ####读取分支 label: master #rabbitmq相关配置<-------------------------- rabbitmq: host: localhost port: 5672 username: guest password: guest #服务注册到eureka地址 eureka: client: service-url: defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka ##rabbitmq相关配置,暴露bus刷新配置的端点<-------------------------- management: endpoints: #暴露bus刷新配置的端点 web: exposure: include: 'bus-refresh'
给cloud-config-client-3355客户端添加消息总线支持
POM
<!--添加消息总线RabbitNQ支持--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-bus-amap</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org-springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId> </dependency>YML
server: port: 3355 spring: application: name: config-client cloud: #Config客户端配置 config: label: master #分支名称 name: config #配置文件名称 profile: dev #读取后缀名称 上述3个综合:master分支上config-dev.yml的配置文件被读取http://config-3344.com:3344/master/config-dev.yml uri: http://localhost:3344 #配置中心地址k #rabbitmq相关配置 15672是Web管理界面的端口;5672是MQ访问的端口<---------------------- rabbitmq: host: localhost port: 5672 username: guest password: guest #服务注册到eureka地址 eureka: client: service-url: defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka # 暴露监控端点 management: endpoints: web: exposure: include: "*"给cloud-config-client-3366客户端添加消息总线支持
POM
<!--添加消息总线RabbitNQ支持--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-bus-amap</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org-springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId> </dependency>YML
server: port: 3366 spring: application: name: config-client cloud: #Config客户端配置 config: label: master #分支名称 name: config #配置文件名称 profile: dev #读取后缀名称 上述3个综合:master分支上config-dev.yml的配置文件被读取http://config-3344.com:3344/master/config-dev.yml uri: http://localhost:3344 #配置中心地址 #rabbitmq相关配置 15672是Web管理界面的端口;5672是MQ访问的端口<----------------------- rabbitmq: host: localhost port: 5672 username: guest password: guest #服务注册到eureka地址 eureka: client: service-url: defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka # 暴露监控端点 management: endpoints: web: exposure: include: "*"
测试
- 启动
- EurekaMain7001
- ConfigcenterMain3344
- ConfigclientMain3355
- ConfigclicntMain3366
- 运维工程师
- 修改Github上配置文件内容,增加版本号
- 发送POST请求
curl -X POST "http://localhost:3344/actuator/bus-refresh"- —次发送,处处生效
- 配置中心
- 客户端
- —次修改,广播通知,处处生效
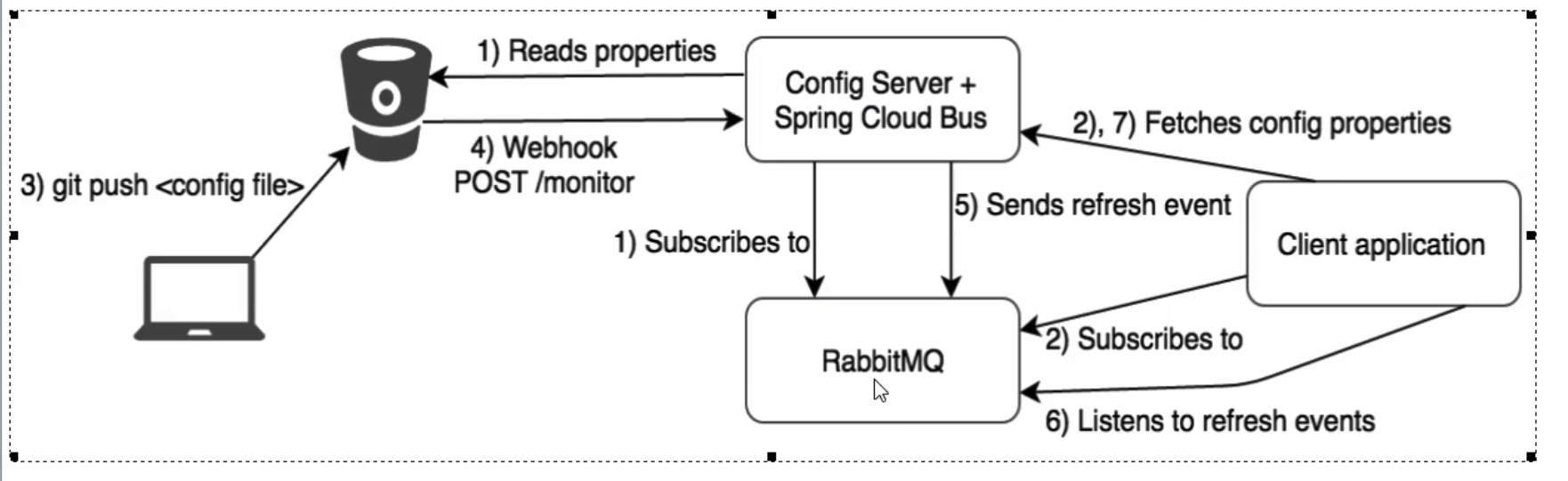
15.4 Bus动态刷新定点通知
不想全部通知,只想定点通知:
- 只通知3355
- 不通知3366
简单一句话
指定具体某一个实例生效而不是全部
/bus-refresh请求不再发送到具体的服务实例上,而是发给config server 。并通过destination参数类指定需要发送更新配置的服务或者实例
案例
我们这里以刷新运行在3355端口上的config-client(配置文件中设定的应用名称)为例,只通知3355,不通知3366
curl -X POST "http://localhost:3344/actuator/bus-refresh/config-client:3355
通知总结
16、Spring Cloud Stream消息驱动
16.1 消息驱动概述
什么是Spring Cloud Stream
官方文档:https://spring.io/projects/spring-cloud-stream#overview
Spring Cloud Stream中文手册:https://m.wang1314.com/doc/webapp/topic/20971999.html
- 官方定义Spring Cloud Stream是一个构建消息驱动微服务的框架;
- 应用程序通过inputs或者 outputs 来与Spring Cloud Stream中binder对象交互。通过我们配置来binding(绑定),而
Spring Cloud Stream的binder对象负责与消息中间件交互。所以,我们只需要搞清楚如何与Spring Cloud Stream交互就可以方便使用消息驱动的方式; - 通过使用Spring Integration来连接消息代理中间件以实现消息事件驱动;
- Spring Cloud Stream为一些供应商的消息中间件产品提供了个性化的自动化配置实现,引用了发布-订阅、消费组、分区的三个核心概念;
- 目前仅支持RabbitMQ、 Kafka;
- 一句话:屏蔽底层消息中间件的差异,降低切换成本,统一消息的编程模型。
为什么引入Stream
常见MQ(消息中间件):
- ActiveMQ
- RabbitMQ
- RocketMQ
- Kafka
有没有一种新的技术诞生,让我们不再关注具体MQ的细节,我们只需要用一种适配绑定的方式,自动的给我们在各种MQ内切换。(类似于Hibernate)
设计思想
标准MQ
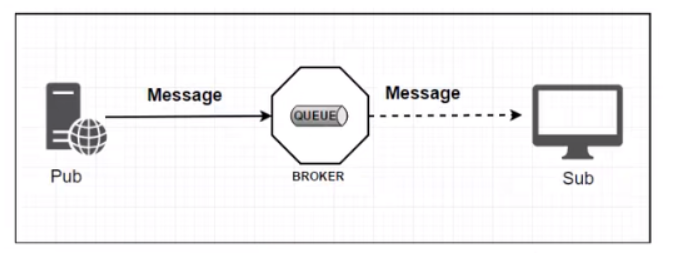
- 生产者/消费者之间靠消息媒介传递信息内容:Message
- 消息必须走特定的通道:MessageChannel
- 消息通道里的消息如何被消费呢?谁负责收发处理?---消息通道MessageChannel的子接口SubscribeChannel,由MessageHandler消息处理器所订阅
为什么用Cloud Stream
- 比方说我们用到了RabbitMQ和Kafka,由于这两个消息中间件的架构上的不同,像RabbitMQ有exchange,kafka有Topic和Partitions分区。
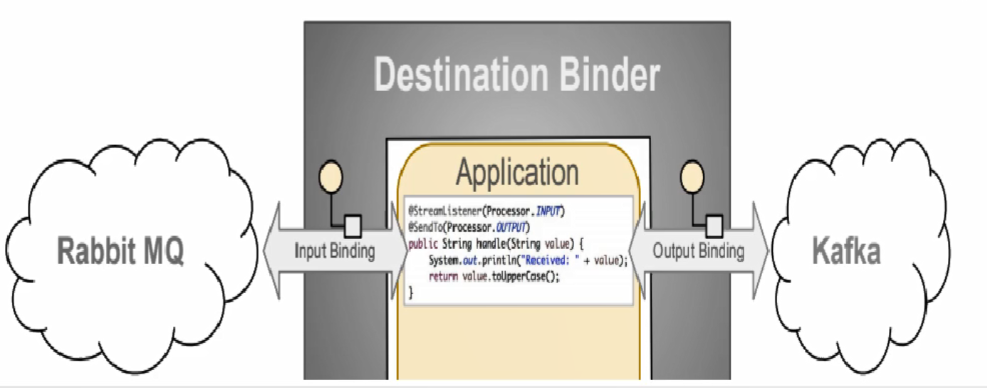
- 这些中间件的差异性导致我们实际项目开发给我们造成了一定的困扰,我们如果用了两个消息队列的其中一种,后面的业务需求,我想往另外一种消息队列进行迁移,这时候无疑就是一个灾难性的,一大堆东西都要重新推倒重新做,因为它跟我们的系统耦合了,这时候
Spring Cloud Stream给我们提供了—种解耦合的方式。
Stream凭什么可以统一底层差异
- 在没有绑定器这个概念的情况下,我们的SpringBoot应用要直接与消息中间件进行信息交互的时候,由于各消息中间件构建的初衷不同,它们的实现细节上会有较大的差异性通过定义绑定器作为中间层,完美地实现了应用程序与消息中间件细节之间的隔离。通过向应用程序暴露统一的Channel通道,使得应用程序不需要再考虑各种不同的消息中间件实现。
- 通过定义绑定器Binder作为中间层,实现了应用程序与消息中间件细节之间的隔离。
Binder
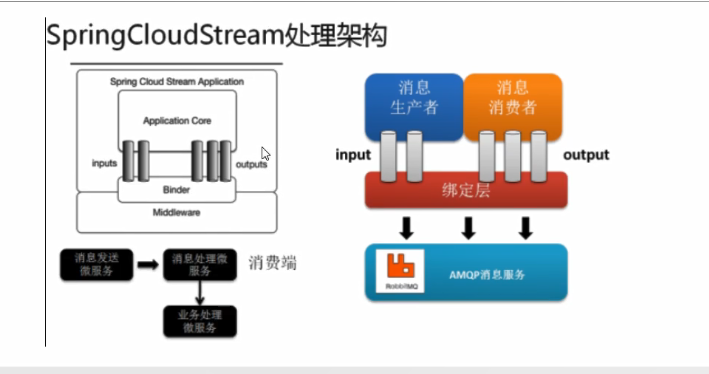
- INPUT适用于消费者
- OUTPUT适用于生产者
Stream中的消息通讯方式遵循了发布-订阅模式
- Topic主题进行广播:
- 在RabbitMQ就是Exchange
- 在Kafka中就是Topic
Spring Cloud Stream标准流程套路
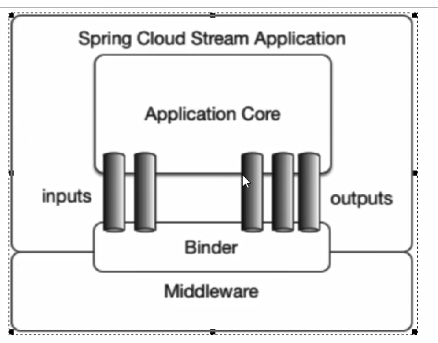
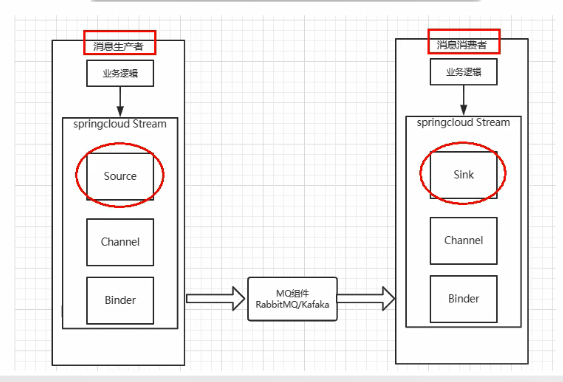
- Binder:很方便的连接中间件,屏蔽差异
- Channel:通道,是队列Queue的一种抽象,在消息通讯系统中就是实现存储和转发的媒介,通过channel对队列进行配置
- Source和Sink:简单的可理解为参照对象是Springcloud
- Stream自身,从Stream发布消息就是输出,接受消息就是输入
编码API和常用注解

| 组成 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Middleware | 中间件,目前只支持RabbitMQ和Kafka |
| Binder | Binder是应用与消息中间件之间的封装,目前实行了Kafka和RabbitMQ的Binder,通过Binder可以很方便的连接中间件,可以动态的改变消息类型(对应于Kafka的topic,RabbitMQ的exchange),这些都可以通过配置文件来实现 |
| @Input | 注解标识输入通道,通过该输乎通道接收到的消息进入应用程序 |
| @Output | 注解标识输出通道,发布的消息将通过该通道离开应用程序 |
| @StreamListener | 监听队列,用于消费者的队列的消息接收 |
| @EnableBinding | 指信道channel和exchange绑定在一起 |
16.2 案例说明
RabbitMQ环境已经OK!
新建三个子模块
cloud-stream-rabbitmq-provider8801,作为生产者进行消息模块cloud-stream-rabbitmq-consumer8802,作为消费者接受模块cloud-stream-rabbitmq-consumer8803,作为消费者接受模块
16.3 消息驱动之生产者
新建module:cloud-stream-rabbitmq-provider8801
POM
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>springcloud2020</artifactId>
<groupId>com.gyz.clouddemo</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>cloud-stream-rabbitmq-provider8801</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-stream-rabbit</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--基础配置-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
YML
server:
port: 8801
spring:
application:
name: cloud-stream-provider
cloud:
stream:
binders: # 在此处配置要绑定的rabbitmq的服务信息;
defaultRabbit: # 表示定义的名称,用于于binding整合
type: rabbit # 消息组件类型
environment: # 设置rabbitmq的相关的环境配置
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: localhost
port: 5672
username: guest
password: guest
bindings: # 服务的整合处理
output: # 这个名字是一个通道的名称
destination: studyExchange # 表示要使用的Exchange名称定义
content-type: application/json # 设置消息类型,本次为json,文本则设置“text/plain”
binder: defaultRabbit # 设置要绑定的消息服务的具体设置
eureka:
client: # 客户端进行Eureka注册的配置
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka
instance:
lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds: 2 # 设置心跳的时间间隔(默认是30秒)
lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds: 5 # 如果现在超过了5秒的间隔(默认是90秒)
instance-id: send-8801.com # 在信息列表时显示主机名称
prefer-ip-address: true # 访问的路径变为IP地址
主启动类
@SpringBootApplication
public class StreamMQMain8801 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(StreamMQMain8801.class, args);
}
}
业务类
public interface IMessageProvider {
public String send();
}
import com.gyz.clouddemo.service.IMessageProvider;
import org.springframework.cloud.stream.annotation.EnableBinding;
import org.springframework.cloud.stream.messaging.Source;
import org.springframework.messaging.MessageChannel;
import org.springframework.messaging.support.MessageBuilder;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.UUID;
/**
* @Description //@EnableBinding(Source.class):定义消息推送通道
* @Author GongYuZhuo
* @Date 2021/7/26 22:22
* @Version 1.0.0
*/
@EnableBinding(Source.class)
public class MessageProviderImpl implements IMessageProvider {
/**消息发送管道 */
@Resource
private MessageChannel output;
@Override
public String send() {
String serial = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
output.send(MessageBuilder.withPayload(serial).build());
System.out.println("*****serial: " + serial);
return serial;
}
}
Controller
@RestController
public class SendMessageController {
@Resource
private IMessageProvider messageProvider;
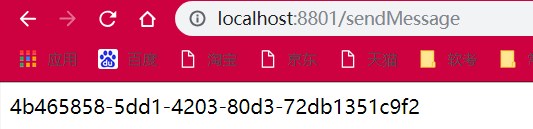
@GetMapping(value = "/sendMessage")
public String sendMessage() {
return messageProvider.send();
}
}
测试
启动
cloud-eureka-server7001服务启动 RabpitMq
- rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management
- http://localhost:15672/
启动
cloud-stream-rabbitmq-provider8801服务访问 - http://localhost:8801/sendMessage
16.4 消息驱动之消费者
新建Module:cloud-stream-rabbitmq-consumer8802
POM
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>springcloud2020</artifactId>
<groupId>com.gyz.clouddemo</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>cloud-stream-rabbitmq-consumer8802</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-stream-rabbit</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--基础配置-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
YML
server:
port: 8802
spring:
application:
name: cloud-stream-consumer
cloud:
stream:
binders: # 在此处配置要绑定的rabbitmq的服务信息;
defaultRabbit: # 表示定义的名称,用于于binding整合
type: rabbit # 消息组件类型
environment: # 设置rabbitmq的相关的环境配置
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: localhost
port: 5672
username: guest
password: guest
bindings: # 服务的整合处理
input: # 这个名字是一个通道的名称
destination: studyExchange # 表示要使用的Exchange名称定义
content-type: application/json # 设置消息类型,本次为对象json,如果是文本则设置“text/plain”
binder: defaultRabbit # 设置要绑定的消息服务的具体设置
eureka:
client: # 客户端进行Eureka注册的配置
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka
instance:
lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds: 2 # 设置心跳的时间间隔(默认是30秒)
lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds: 5 # 如果现在超过了5秒的间隔(默认是90秒)
instance-id: receive-8802.com # 在信息列表时显示主机名称
prefer-ip-address: true # 访问的路径变为IP地址
主启动类
@SpringBootApplication
public class StreamMQMain8802 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(StreamMQMain8802.class, args);
}
}
监听类
/**
* @Description 监听类
* @Author GongYuZhuo
* @Date 2021/7/26 22:59
* @Version 1.0.0
*/
@Component
@EnableBinding(Sink.class)
public class ReceiveMessageListenerController {
@Value("${server.port}")
private String serverPort;
@StreamListener(Sink.INPUT)
public void input(Message<String> message) {
System.out.println("消费者1号,----->接受到的消息: " + message.getPayload() + "\t port: " + serverPort);
}
}
测试
- 启动EurekaMain7001
- 启动StreamMQMain8801
- 启动StreamMQMain8802
- 访问 - http://localhost:8801/sendMessage ;8801发送8802接收消息
16.5 Stream之消息重复消费
依照8802,clone出来一份运行8803。
启动
- RabbitMQ
- 服务注册 - 7001
- 消息生产 - 8801
- 消息消费 - 8802
- 消息消费 - 8803
运行后有两个问题
- 重复消费问题
- 消息持久化问题
消费
- 8802/8803同时收到了消息,存在重复消费的问题。http://localhost:8801/sendMessage
- 如何解决?分组和持久化属性group
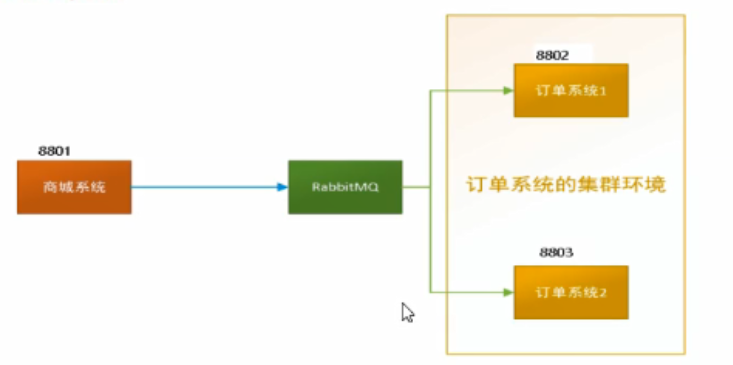
生产实际案例
比如在如下场景中,订单系统我们做集群部署,都会从RabbitMQ中获取订单信息,那如果一个订单同时被两个服务获取到,那么就会造成数据错误,我们得避免这种情况。这时我们就可以使用Stream中的消息分组来解决。
分组(重要)
原理:微服务应用放置于同一个group中,就能够保证消息只会被其中一个应用消费一次。不同的组是可以消费的,同一个组内会发生竞争关系,只有其中一个可以消费。
8802/8803都变成不同组,group两个不同
group:gyzA,gyzB
8802修改YML:

8803修改YML:

结论:还是有重复消费的问题
8802/8803实现了轮询分组,每次只有一个消费者。8801模块的发的消息只能被8802或者8803其中一个接受到,这样避免了重复消费
8803/8802都变成相同组,group两个相同
- group:gyzA
- 修改8802YML:group:gyzA
- 修改8803YML:group:gyzA
- 我们结论:同一个组的多个微服务实例,每次只会有一个拿到
持久化(重要)
- 通过上述,解决了重复消费的问题,再看看持久化
- 停止8802/8803;除掉8802的分组group:gyzA;8003的分组属性保留
- 8801先发送4条消息到rabbitmq
- 先启动8802,无分组属性配置,后台没有打出来消息
- 再启动8803,有分组属性配置,后台打出来了MQ上的消息(消息持久化体现)
17、Spring Cloud Sleuth分布式链路跟踪
17.1 概述
为什么会出现这个技术?需要解决那些问题?
在微服务框架中,一个由客户端发起的请求在后端系统中会经过多个不同的的服务节点调用来协同产生最后的请求结果,每一个前段请求都会形成一条复杂的分布式服务调用链路,链路中的任何一环出现高延时或错误都会引起整个请求最后的失败。

是什么
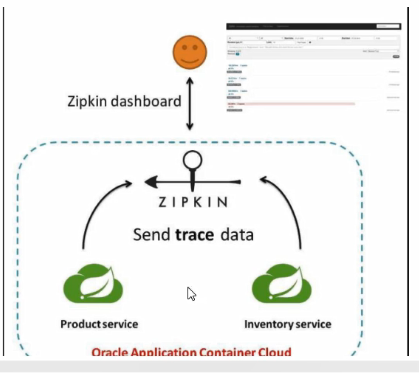
Spring Cloud Sleuth提供了一套完整的服务跟踪的解决方案,在分布式系统中提供追踪解决方案并且兼容支持了zipkin
解决
17.2 Sleuth之zipkin搭建安装
zipkin
下载
- SpringCloud从F版起已不需要自己构建Zipkin Server了,只需调用jar包即可
- https://dl.bintray.com/openzipkin/maven/io/zipkin/java/zipkin-server/
- zipkin-server-2.12.9-exec.jar
运行jar
java -jar zipkin-server-2.12.9-exec.jar
运行控制台
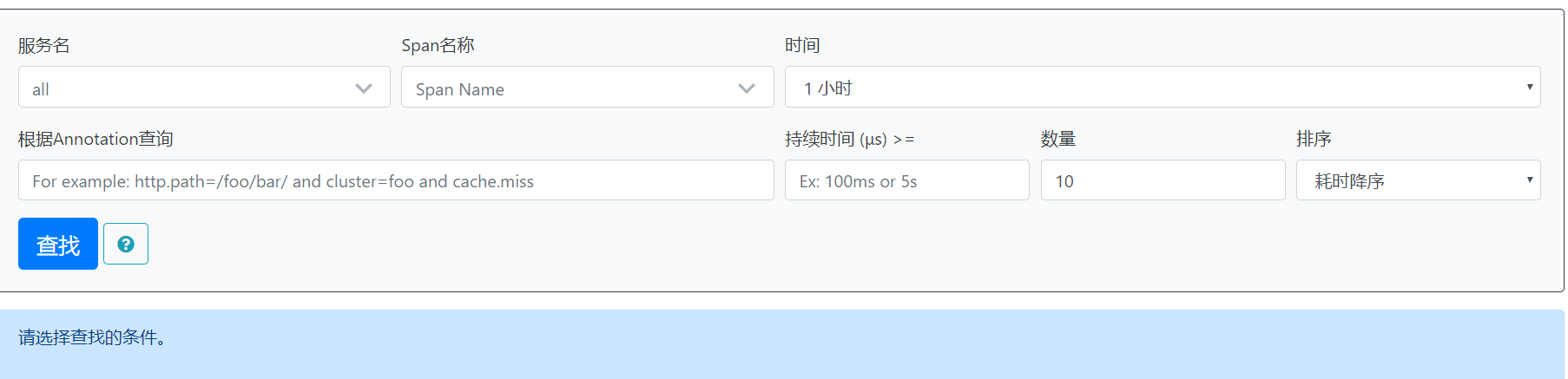
术语
完整的调用链路
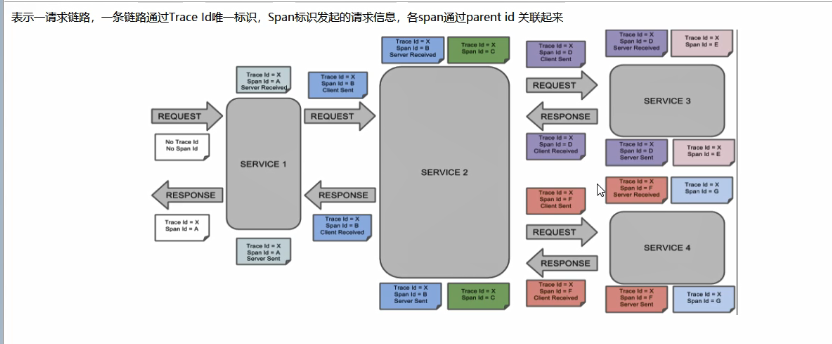
—条链路通过Trace ld唯一标识,Span标识发起的请求信息,各span通过parent id关联起来
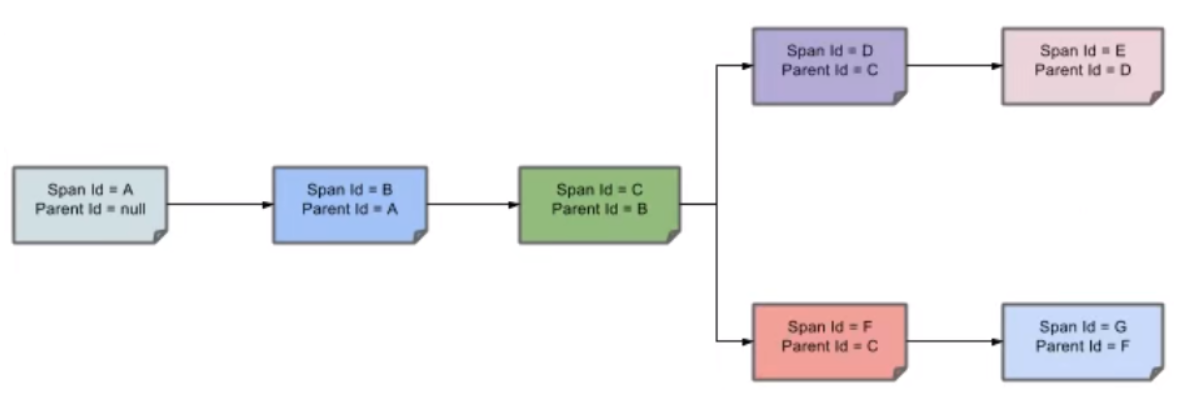
名词解释
- Trace:类似于树结构的Span集合,表示一条调用链路,存在唯一标识
- span:表示调用链路来源,通俗的理解span就是一次请求信息
17.3 Sleuth链路监控展现
服务提供者
修改cloud-provider-payment8001
POM
<!--包含了sleuth+zipkin-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-zipkin</artifactId>
</dependency>
YML
server:
port: 8001
spring:
application:
name: cloud-payment-service
zipkin:
base-url: http://localhost:9411
sleuth:
sampler:
#采样率值介于 0 到 1 之间,1 则表示全部采集
probability: 1
datasource:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource # 当前数据源操作类型
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver # mysql驱动包
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db29?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
username: root
password: root
mybatis:
mapperLocations: classpath:mapper/*.xml
type-aliases-package: com.gyz.clouddemo.entity # 所有Entity别名类所在包
eureka:
client:
#表示是否将自己注册进Eurekaserver默认为true。
register-with-eureka: true
#是否从EurekaServer抓取已有的注册信息,默认为true。单节点无所谓,集群必须设置为true才能配合ribbon使用负载均衡
fetchRegistry: true
service-url:
defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka, http://eureka7002.com:7002/eureka
instance:
instance-id: payment8001 #显示的IP地址,换成可读性高的名字
prefer-ip-address: true
#Eureka客户端向服务端发送心跳的时间间隔,单位为秒(默认是30秒)
lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds: 1
#Eureka服务端在收到最后一次心跳后等待时间上限,单位为秒(默认是90秒),超时将剔除服务
lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds: 2
#logging:
# level:
# org:
# springframework:
# boot:
# autoconfigure: ERROR
业务类PaymentController新增如下方法
@GetMapping("/payment/zipkin")
public String paymentZipkin() {
return "hi,i`am paymentzipkin server fall back.welcome to halashao";
}
服务消费者
修改cloud-comsumer-order80
POM:同提供者一样,加入依赖包
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-zipkin</artifactId> </dependency>YML
server: port: 80 spring: application: name: cloud-order-service zipkin: base-url: http://localhost:9411 sleuth: sampler: probability: 1 eureka: client: #表示是否将自己注册进Eurekaserver默认为true。 register-with-eureka: true #是否从EurekaServer抓取已有的注册信息,默认为true。单节点无所谓,集群必须设置为true才能配合ribbon使用负载均衡 fetchRegistry: true service-url: defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka, http://eureka7002.com:7002/eureka业务类OrderController
/** * @Description zipkin+sleuth * @return java.lang.String */ @GetMapping("/consumer/payment/zipkin") public String paymentZipkin() { String result = restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:8001" + "/payment/zipkin/", String.class); return result; }测试
- 依次启动7001/8001/80
- 打开浏览器访问:http://localhost:9411