Sharding-JDBC分库分表
1. 什么是 ShardingSphere ?
- 一套开源的分布式数据库中间件解决方案
- 有三个产品: Sharding-JDBC 和 Sharding-Proxy 和 Sharding-Sidecar(规划中)
- 定位为关系型数据库中间件,合理在分布式环境下使用关系型数据库操作
2. 什么是分库分表 ?
数据库数据量不可控的,随着时间和业务发展,造成表里面数据越来越多,如果再去对数 据库表 curd 操作时候,造成性能问题。
解决由于数据量过大而造成数据库性能降低问题的方案:
- 解决方案 1:通过提升服务器硬件能力来提高数据处理能力,比如增加存储容量 、CPU等,这种方案成本很高,并且如果瓶颈在 MySQL本身那么提高硬件也是有限的。
- 解决方案 2:分库分表!
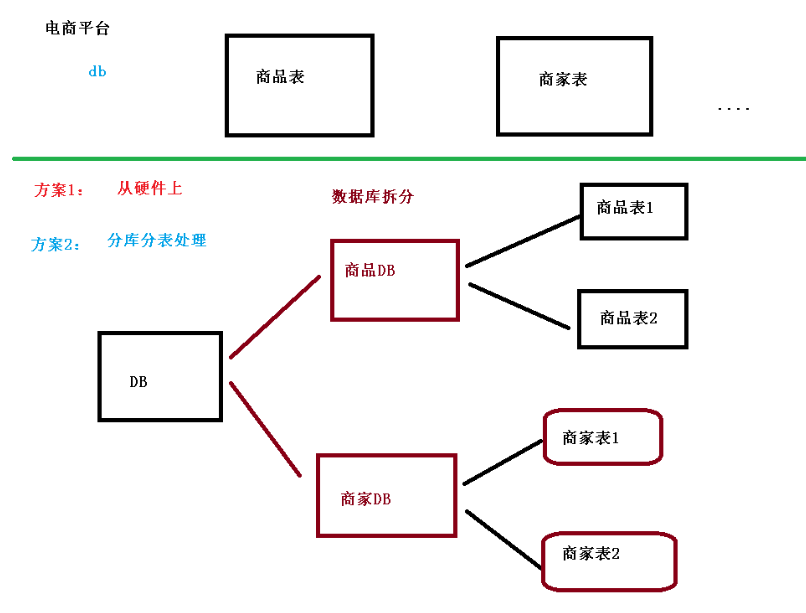
3. 分库分表的方式
分库分表有两种方式:垂直切分和水平切分
- 垂直切分:垂直分表和垂直分库
- 水平切分:水平分表和水平分库
垂直分表
操作数据库中某张表,把这张表中一部分字段数据存到一张新表里面,再把这张表另一 部分字段数据存到另外一张表里面。
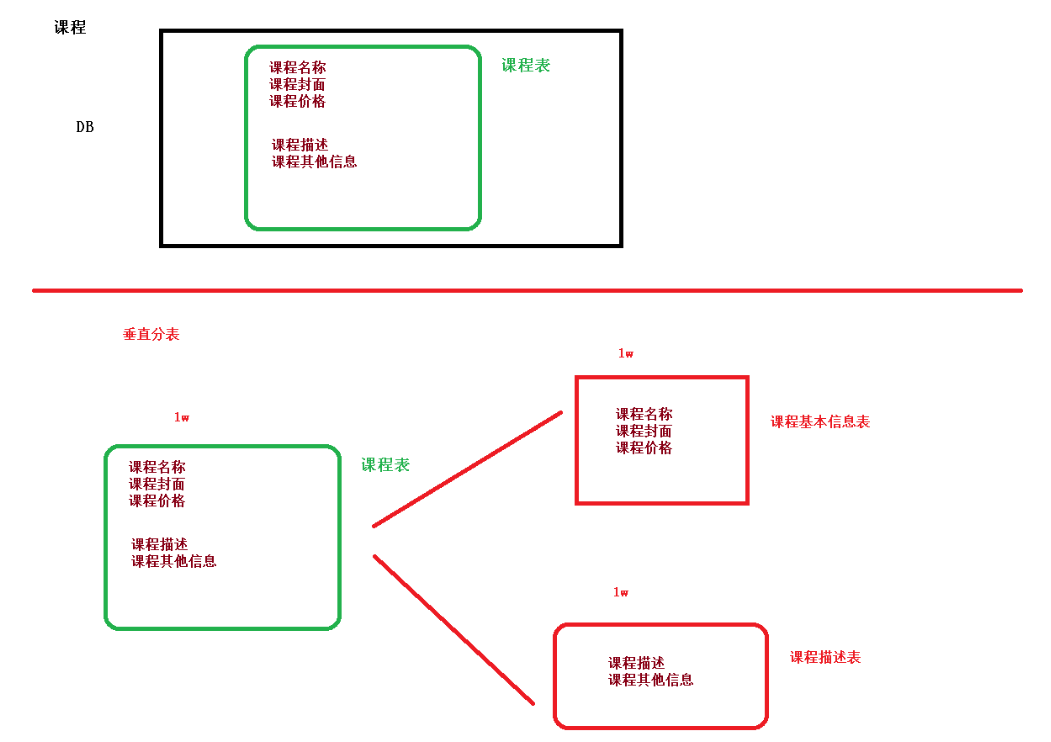
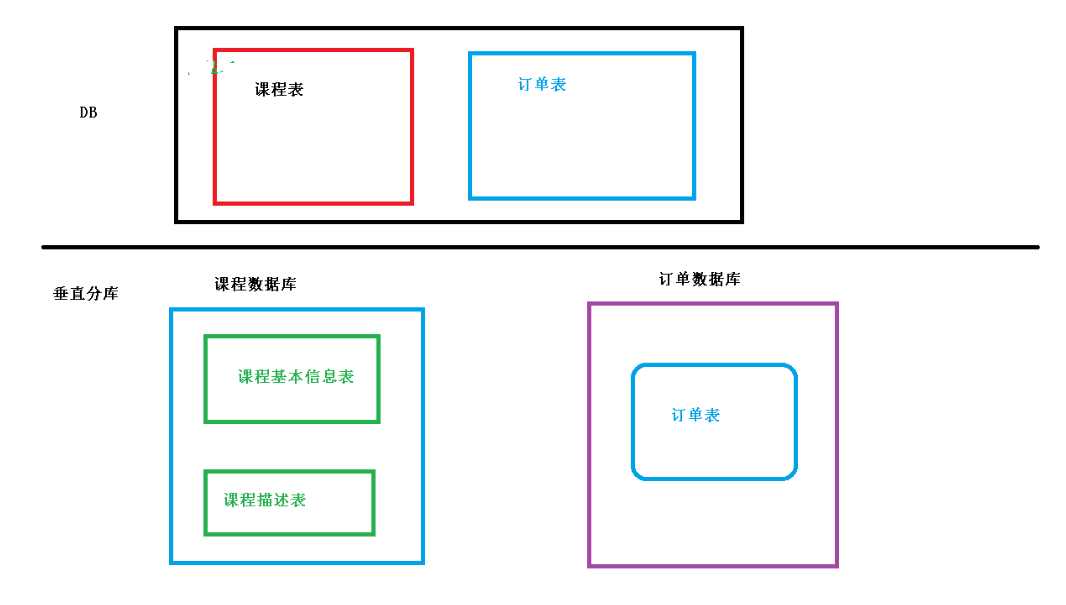
垂直分库
把单一数据库按照业务进行划分,专库专表。
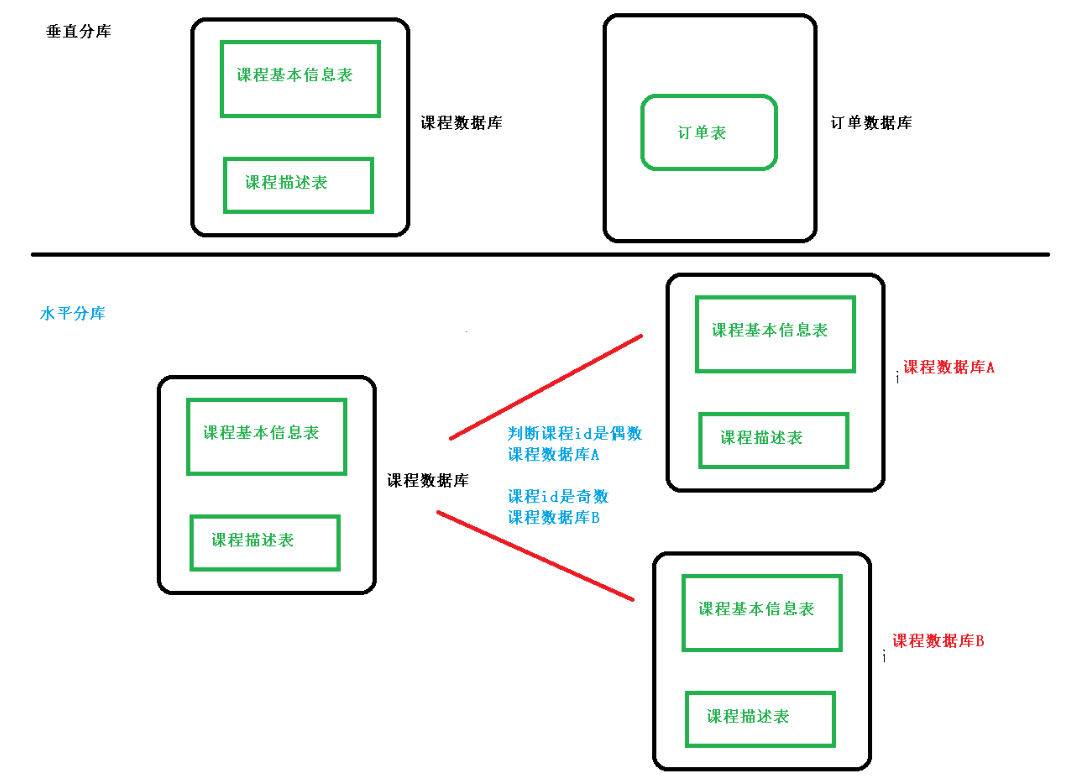
水平分库
经过垂直分库后,数据库性能问题得到一定程度的解决,但是随着业务量的增长,单库存储数据已经超出预估。并且访问非常频繁,此时该如何优化?从业务角度分析,目前情况已经无法再次垂直分库。尝试水平分库。
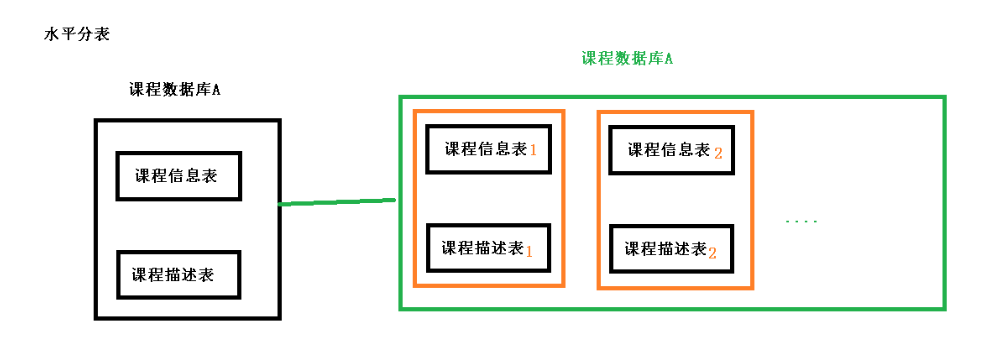
水平分表
其目的也是为解决单表数据量大 的问题,如下图:
4. 分库分表应用和问题
应用
- 在数据库设计时候考虑垂直分库和垂直分表
- 随着数据库数据量增加,不要马上考虑做水平切分,首先考虑缓存处理,读写分离,使 用索引等等方式,如果这些方式不能根本解决问题了,再考虑做水平分库和水平分表
分库分表问题
- 跨节点连接查询问题(分页、排序)
- 多数据源管理问题
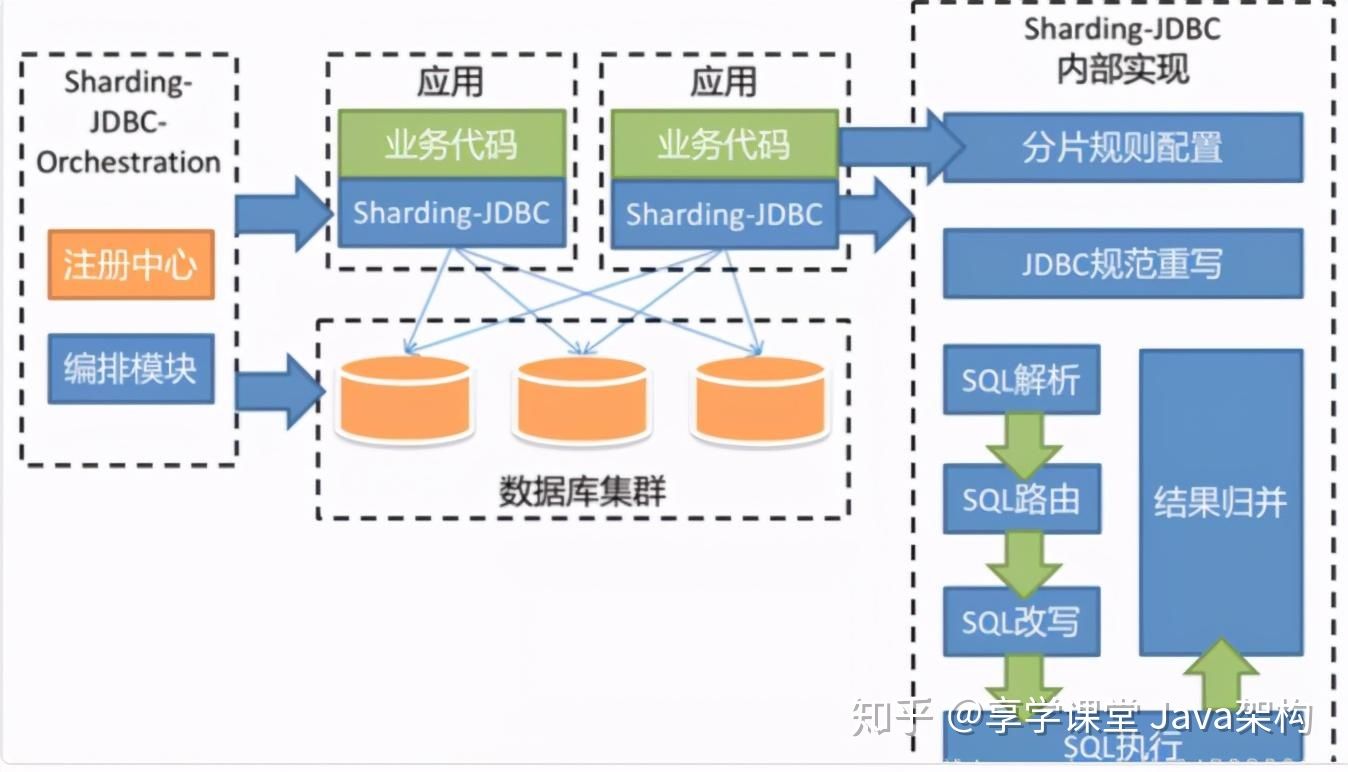
5. Sharding-JDBC 简介
概念:定位为轻量级Java框架,在Java的JDBC层提供的额外服务。 它使用客户端直连数据库,以jar包形式提供服务,无需额外部署和依赖,可理解为增强版的JDBC驱动,完全兼容JDBC和各种ORM框架。
主要目的是:简化对分库分表之后数据相关操作
6. Sharding-JDBC 实现水平分表
6.1. (一)搭建环境
技术: SpringBoot 2.2.1+ MyBatisPlus + Sharding-JDBC + Druid 连接池
具体 Maven 依赖:
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>1.1.20</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.shardingsphere</groupId> <artifactId>sharding-jdbc-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>4.0.0-RC1</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.baomidou</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>3.0.5</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies>按照水平分表来创建数据库
创建数据库 course_db
创建表 course_1 、 course_2
约定规则:如果添加的课程 id 为偶数添加到 course_1 中,奇数添加到 course_2 中。
SQL 如下:
create database course_db; use course_db; create table course_1 ( cid bigint(20) primary key , cname varchar(50) not null, user_id bigint(20) not null , status varchar(10) not null ) engine = InnoDB; create table course_2 ( cid bigint(20) primary key , cname varchar(50) not null, user_id bigint(20) not null , status varchar(10) not null ) engine = InnoDB;
6.2. (二)配置对应实体类以及 Mapper
entity:
/**
* @Description Course实体类
* @Author GongYuZhuo
* @Date 2021/7/10 16:50
* @Version 1.0.0
*/
@Data
public class Course {
private Long cid;
private String cname;
private Long userId;
private String status;
}mapper:
@Repository
public interface CourseMapper extends BaseMapper<Course> {
}6.3. (三)配置 Sharding-JDBC 分片策略
application.properties 内容:
# 配置真实数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=m1
# 配置数据源具体内容,包含连接池,驱动,地址,用户名和密码 characterEncoding=utf-8解决表里中文乱码
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/course_db?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&&characterEncoding=utf-8
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.password=
# 指定course表分布的情况,配置表在哪个数据库里,表的名称都是什么 m1.course_1,m1.course_2
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.actual-data-nodes=m1.course_$->{1..2}
# 指定 course 表里面主键 cid 的生成策略 SNOWFLAKE(雪花算法)
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.key-generator.column=cid
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
# 配置分表策略 约定 cid 值偶数添加到 course_1 表,如果 cid 是奇数添加到 course_2 表
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.table-strategy.inline.sharding-column=cid
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.table-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=course_$->{cid % 2 + 1}
#打开sql输出日志
spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show=true6.4. (四)测试代码运行
package com.gyz.shardingjdbcdemo;
import com.gyz.shardingjdbcdemo.entity.Course;
import com.gyz.shardingjdbcdemo.mapper.CourseMapper;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
class ShardingjdbcdemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private CourseMapper courseMapper;
@Test
public void addCourse() {
Course course = new Course();
course.setCname("测试水平分表");
course.setStatus("01");
course.setUserId(100L);
courseMapper.insert(course);
}
}发现报错,提示信息:
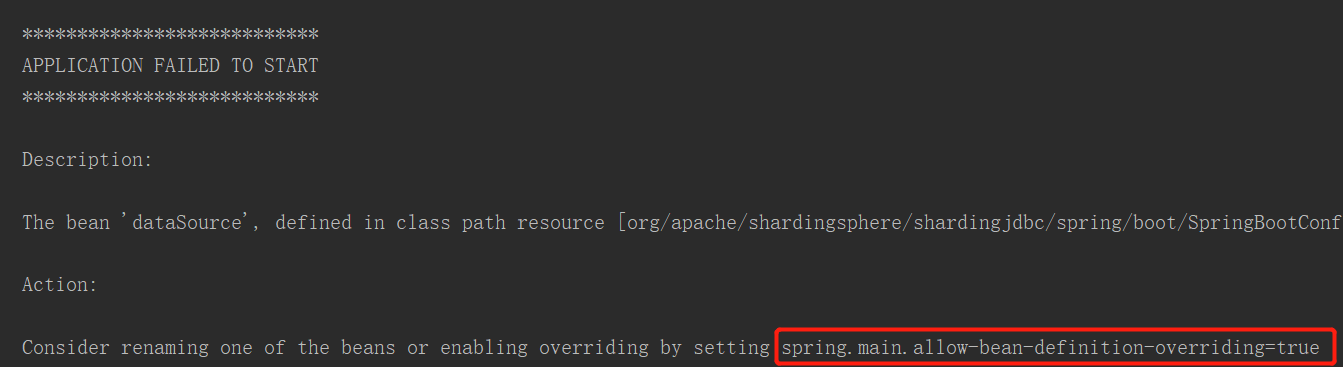
主要是因为一个实体类对应两个表不知插数据到那。配置红圈信息到application.properties。
#一个实体类对应两张表,覆盖
spring.main.allow-bean-definition-overriding=true再次运行:

查询一下看看:
@Test
public void queryCourse(){
QueryWrapper<Course> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.eq("cid",620675708724707329L);
courseMapper.selectOne(wrapper);
}查询成功:

7. Sharding-JDBC 实现水平分库
需求:
- 创建两个数据库,edu_db_1、edu_db_2。
- 每个库中包含:course_1、course_2。
- 数据库规则:userid 为偶数添加到 edu_db_1 库,奇数添加到 edu_db_2。
- 表规则:如果添加的 cid 为偶数添加到 course_1 中,奇数添加到 course_2 中。
7.1. (一)创建数据库和表结构
create database edu_db_1;
create database edu_db_2;
create table course_1 (
`cid` bigint(20) primary key,
`cname` varchar(50) not null,
`user_id` bigint(20) not null,
`status` varchar(10) not null
);
create table course_2 (
`cid` bigint(20) primary key,
`cname` varchar(50) not null,
`user_id` bigint(20) not null,
`status` varchar(10) not null
);7.2. (二)在 SpringBoot 配置文件配置数据库分片规则
# 配置真实数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=m1,m2
# 配置第一个数据源具体内容,包含连接池,驱动,地址,用户名和密码
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/edu_db_1?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&&characterEncoding=utf-8
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.password=
#配置第二个数据源具体内容,包含连接池,驱动,地址,用户名和密码
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/edu_db_2?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&&characterEncoding=utf-8
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.password=
#指定数据库分布情况,数据库里面表分布情况
# m1 m2 course_1 course_2
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.actual-data-nodes=m$->{1..2}.course_$->{1..2}
# 指定course表里面主键cid 生成策略 SNOWFLAKE
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.key-generator.column=cid
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
# 指定表分片策略 约定cid值偶数添加到course_1表,如果cid是奇数添加到course_2表
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.table-strategy.inline.sharding-column=cid
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.table-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=course_$->{cid % 2 + 1}
# 指定数据库分片策略 约定user_id是偶数添加m1,是奇数添加m2
#spring.shardingsphere.sharding.default-database-strategy.inline.sharding-column=user_id
#spring.shardingsphere.sharding.default-database-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=m$->{user_id % 2 + 1}
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.database-strategy.inline..sharding-column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.database-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=m$->{user_id % 2 + 1}
# 打开sql输出日志
spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show=true
#一个实体类对应两张表,覆盖
spring.main.allow-bean-definition-overriding=true测试代码运行:
/**
* @return void
* @Description 水平分库测试添加
*/
@Test
public void addCourse1() {
Course course = new Course();
//cid由我们设置的策略,雪花算法进行生成
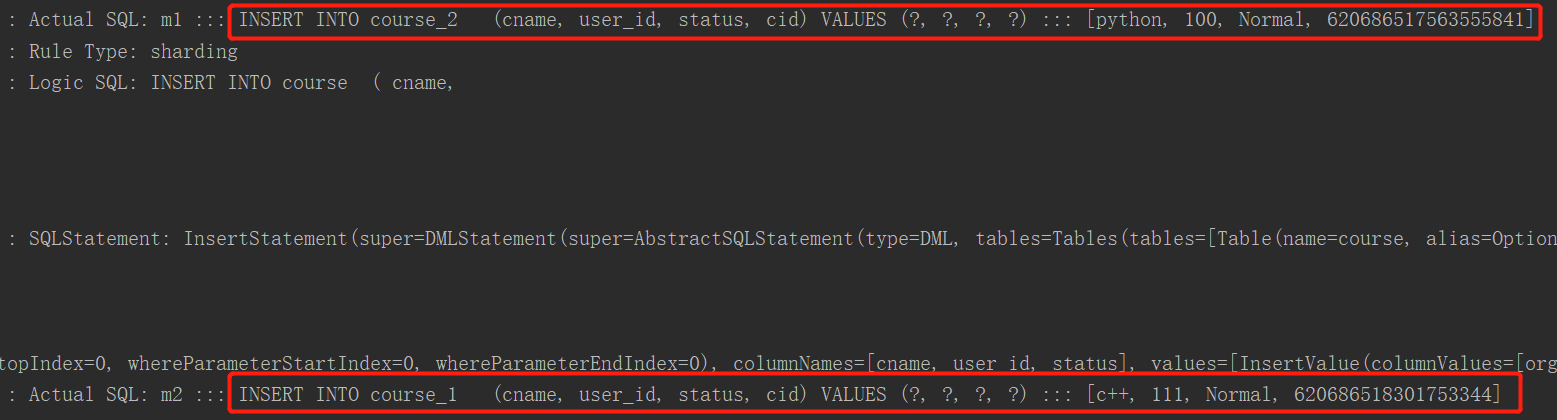
course.setCname("python");
//分库根据user_id
course.setUserId(100L);
course.setStatus("Normal");
courseMapper.insert(course);
course.setCname("c++");
course.setUserId(111L);
courseMapper.insert(course);
}运行结果:
8. Sharding-JDBC 实现垂直分库
8.1. (一)建库建表
垂直分库就是专库专表
再创建一个 user_db 数据库。当我们查询用户信息就去 user_db,课程信息就去 edu_db_1、edu_db_2。
create database user_db;
use user_db;
create table t_user(
`user_id` bigint(20) primary key,
`username` varchar(100) not null,
`status` varchar(50) not null
);8.2. (二)配置对应实体类和 Mapper
@TableName("t_user")不配置的话找不到表!
@Data
@TableName("t_user")
public class User {
private Long userId;
private String username;
private String status;
}@Repository
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {
}application.properties 内容:
# 垂直分库
# 配置真实数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=m1,m2,m0
# 配置第一个数据源具体内容,包含连接池,驱动,地址,用户名和密码
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/edu_db_1?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&&characterEncoding=utf-8
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.password=
#配置第二个数据源具体内容,包含连接池,驱动,地址,用户名和密码
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/edu_db_2?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&&characterEncoding=utf-8
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.password=
#配置第二个数据源具体内容,包含连接池,驱动,地址,用户名和密码
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m0.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m0.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m0.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/user_db?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&&characterEncoding=utf-8
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m0.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m0.password=
#指定数据库分布情况,数据库里面表分布情况
# m1 m2 course_1 course_2
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.actual-data-nodes=m$->{0}.t_user
# 指定course表里面主键cid 生成策略 SNOWFLAKE
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.key-generator.column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
# 指定表分片策略
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.table-strategy.inline.sharding-column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.table-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=t_user
#指定数据库分布情况,数据库里面表分布情况
# m1 m2 course_1 course_2
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.actual-data-nodes=m$->{1..2}.course_$->{1..2}
# 指定course表里面主键cid 生成策略 SNOWFLAKE
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.key-generator.column=cid
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
# 指定表分片策略 约定cid值偶数添加到course_1表,如果cid是奇数添加到course_2表
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.table-strategy.inline.sharding-column=cid
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.table-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=course_$->{cid % 2 + 1}
# 指定数据库分片策略 约定user_id是偶数添加m1,是奇数添加m2
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.database-strategy.inline.sharding-column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.database-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=m$->{user_id % 2 + 1}
# 打开sql输出日志
spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show=true
#一个实体类对应两张表,覆盖
spring.main.allow-bean-definition-overriding=true8.3. (三)测试代码
@Test
public void addUser(){
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("Jack");
user.setStatus("Normal");
userMapper.insert(user);
}
@Test
public void findUser() {
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.eq("user_id", 620697113113657345L);
userMapper.selectOne(wrapper);
}9. Sharding-JDBC 公共表
概念
- 存储固定数据的表,表数据很少发生变化,查询时经常要进行关联。
- 在每个数据库中都创建出相同结构公共表。
- 操作公共表时,同时操作添加了公共表的数据库中的公共表,添加记录时,同时添加,删除时,同时删除。
9.1. (一)在多个数据库创建表
# use user_db;
# use edu_db_1;
use edu_db_2;
create table t_dict(
`dict_id` bigint(20) primary key,
`status` varchar(100) not null,
`value` varchar(100) not null
);9.2. (二)配置公共表的实体类和 mapper
@Data
@TableName("t_dict")
public class Dict {
private Long dictId;
private String status;
private String value;
}@Repository
public interface DictMapper extends BaseMapper<Dict> {
}application.properties 内容:
# 公共表
# 配置真实数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=m1,m2,m0
# 配置第一个数据源具体内容,包含连接池,驱动,地址,用户名和密码
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/edu_db_1?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&&characterEncoding=utf-8
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.password=
#配置第二个数据源具体内容,包含连接池,驱动,地址,用户名和密码
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/edu_db_2?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&&characterEncoding=utf-8
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m2.password=
#配置第二个数据源具体内容,包含连接池,驱动,地址,用户名和密码
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m0.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m0.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m0.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/user_db?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&&characterEncoding=utf-8
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m0.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m0.password=
# 配置user_db数据库里面t_user 专库专表
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.actual-data-nodes=m0.t_user
# 指定t_user表里面主键user_id 生成策略 SNOWFLAKE
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.key-generator.column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
# 指定表分片策略
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.table-strategy.inline.sharding-column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.table-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=t_user
#指定数据库分布情况,数据库里面表分布情况
# m1 m2 course_1 course_2
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.actual-data-nodes=m$->{1..2}.course_$->{1..2}
# 指定course表里面主键cid 生成策略 SNOWFLAKE
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.key-generator.column=cid
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
# 指定表分片策略 约定cid值偶数添加到course_1表,如果cid是奇数添加到course_2表
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.table-strategy.inline.sharding-column=cid
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.table-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=course_$->{cid % 2 + 1}
# 指定数据库分片策略 约定user_id是偶数添加m1,是奇数添加m2
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.database-strategy.inline.sharding-column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.course.database-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=m$->{user_id % 2 + 1}
# 公共表配置
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.broadcast-tables=t_dict
# 配置主键的生成策略
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_dict.key-generator.column=dict_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_dict.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
# 打开sql输出日志
spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show=true
#一个实体类对应两张表,覆盖
spring.main.allow-bean-definition-overriding=true9.3. (三)测试
@Test
public void addDict() {
Dict dict = new Dict();
dict.setStatus("Normal");
dict.setValue("启用");
dictMapper.insert(dict);
}运行结果:

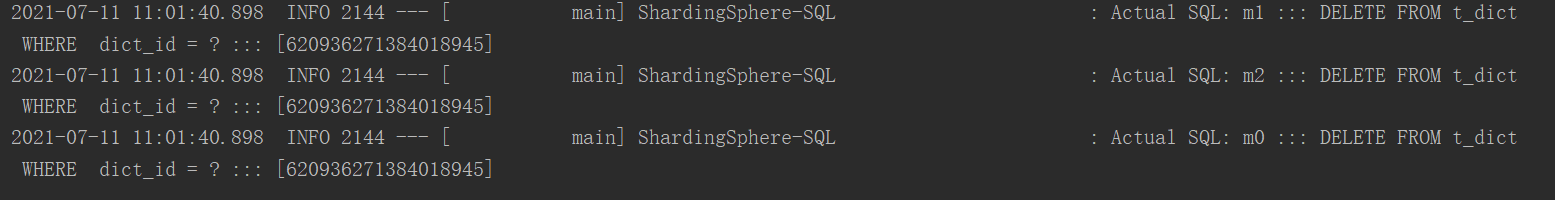
@Test
public void deleteDict() {
QueryWrapper<Dict> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.eq("dict_id", 620936271384018945L);
dictMapper.delete(wrapper);
}运行结果:
10. 什么是读写分离
**主从复制:**当主服务器有写入(update/delete/insert)语句的时候,从服务器自动获取。
**读写分离:**update/delete/insert 操作一台服务器,select 另一台服务器。
10.1. (一)先了解下什么是主从复制
主从复制,是用来建立一个和主数据库完全一样的数据库环境,称为从数据库,主数据库一般是准实时的业务数据库。在赋值过程中,一台服务器充当主服务器,而另外一台服务器充当从服务器。此时主服务器会将更新信息写入到一个特定的二进制文件中。并会维护文件的一个索引用来跟踪日志循环。这个日志可以记录并发送到从服务器的更新中去。当一台从服务器连接到主服务器时,从服务器会通知主服务器从服务器的日志文件中读取最后一次成功更新的位置。然后从服务器会接收从哪个时刻起发生的任何更新,然后锁住并等到主服务器通知新的更新。
10.2. (二)主从复制原理
原理
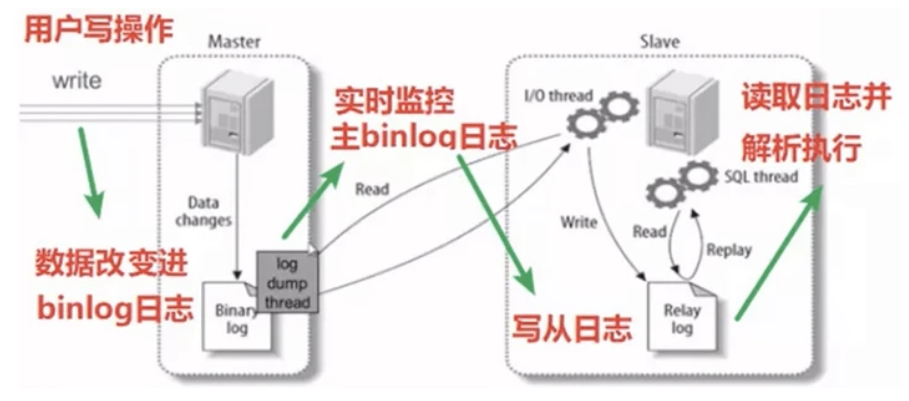
- 主库将变更写入 binlog 日志,然后从库连接到主库之后,从库有一个 IO 线程,将主库的 binlog 日志拷贝到自己本地,写入一个 relay 中继日志(relay log)中。接着从库中有一个 SQL 线程会从中继日志读取 binlog,然后执行 binlog 日志中的内容,也就是在自己本地再次执行一遍 SQL 语句,从而使从服务器和主服务器的数据保持一致。
- 从库会生成两个线程,一个 I/O 线程,一个 SQL 线程; I/O 线程会去请求主库的 binlog,并将得到的 binlog 写到本地的 relay-log(中继日志)文件中; 主库会生成一个 log dump 线程, 用来给从库 I/O 线程传 binlog; SQL 线程,会读取 relay log 文件中的日志,并解析成 sql 语句逐一执行。
- 注意:从库同步主库数据的过程是串行化的,也就是说主库上并行的操作,在从库上会串行执行。
- 由于从库从主库拷贝日志以及串行执行 SQL 的特点,在高并发场景下,从库的数据是有延时的。在实际运用中,时常会出现这样的情况,主库的数据已经有了,可从库还是读取不到,可能要过几十毫秒,甚至几百毫秒才能读取到。
解决主库数据丢失问题
- 半同步复制:解决主库数据丢失问题。也叫 semi-sync 复制,指的就是主库写入 binlog 日志之后,就会强制将数据立即同步到从库,从库将日志写入自己本地的 relay log 之后,接着会返回一个 ack 给主库,主库接收到至少一个从库的 ack 之后才会认为写操作完成了。
解决从库复制延迟的问题
- 并行复制:解决从库复制延迟的问题。指的是从库开启多个线程,并行读取 relay log 中不同库的日志,然后并行存放不同库的日志,这是库级别的并行。
10.3. (三)主从同步延迟问题
MySQL 可以通过命令 show slave status 获知当前是否主从同步正常工作。其中一个重要指标就是 Seconds_Behind_Master,根据输出的 Seconds_Behind_Master 参数的值来判断:
NULL,表示 io_thread 或是 sql_thread 有任何一个发生故障。
0,表示主从复制良好。
正值,表示主从已经出现延时,数字越大表示从库延迟越严重。
10.4. (四)导致主从同步延迟情况
- 主库的从库太多,导致复制延迟。
- 从库硬件比主库差,导致复制延迟。
- 慢 SQL 语句过多。
- 主从复制的设计问题,例如主从复制单线程,如果主库写并发太大,来不及传送到从库,就会导致延迟。Mysql5.7 之后可以支持多线程复制。设置参数
slave_parallel_workers>0和slave_parallel_type='LOGICAL_CLOCK'。 - 网络延迟。
10.5. (五)主从同步解决方案
- 使用 PXC 架构
- 避免一些无用的 IO 消耗,可以上 SSD。
- IO 调度要选择 deadline 模式。
- 适当调整 buffer pool 的大小。
- 避免让数据库进行各种大量运算,数据库只是用来存储数据的,让应用端多分担些压力,或者可以通过缓存来完成。
说到底读写分离就是主库进行写操作,从库进行读操作。具体可以搭配一主一从、一主多从、多主多从。根据业务场景来进行选择。
10.6. (六)搭建一主一从 MySQL 环境
使用的是两台 Centos7 虚拟机,主服务器 IP 为:192.168.3.107,从服务器 IP:192.168.3.108。
MySQL 环境为:8.0.15。
首先我们进入主服务器输入以下命令:
vim /etc/my.cnf在[mysqld]节点下加入:
#设置主mysql的id
server-id = 1
#启用二进制日志
log-bin=mysql-bin
#设置logbin格式
binlog_format = STATEMENT注:也可以加入 binlog-do-db 来指定同步的数据库 ,或者使用 binlog-ignore-db 来忽略同步的数据库,如果不写则同步所有数据库!
然后我们进入从服务器输入以下命令:
vim /etc/my.cnf在[mysqld]节点下加入:
#设置从mysql的id
server-id = 2
#启用中继日志
relay-log = mysql-relay最后我们使用下面命令在主和从都执行,重启 MySQL 服务器。
/etc/init.d/mysqld restart以上完毕之后我们登录主服务器的 MySQL。
mysql -u root -p进入 MySQL 后执行以下命令:
#创建用于主从复制的账号db_sync,密码db_sync
create user 'db_sync'@'%' identified with mysql_native_password by 'db_sync';
#授权
grant replication slave on *.* to 'db_sync'@'%';
#刷新权限
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
然后我们执行以下命令,记得file和position的值!
show master status;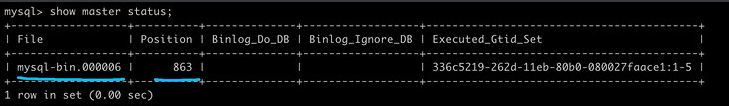
以上完毕之后我们登录从服务器的 MySQL。
mysql -u root -p;进入 MySQL 后执行以下命令:
STOP SLAVE;接着我们输入命令来连接主服务器:
#修改从库指向到主库
# master_host 主ip地址
# master_port 主mysql暴露的端口
# master_user 主mysql的用户名
# master_password 主mysql的密码
# master_log_file 填写刚才查看到的file
# master_log_pos 填写刚才查看到的position
CHANGE MASTER TO
master_host = '192.168.3.107',
master_port = 3306,
master_user = 'db_sync',
master_password = 'db_sync',
master_log_file = 'mysql-bin.000006',
master_log_pos = 863;然后启动我们的 slave:
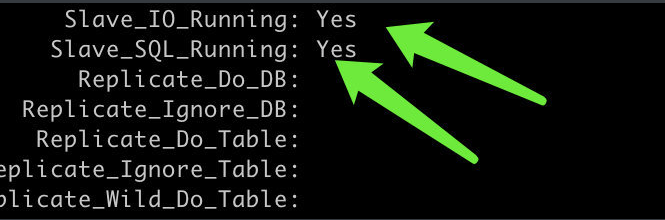
START SLAVE;最后一定要查看一下是否成功!
show slave status \G;Slave_IO_Runing和Slave_SQL_Runing字段值都为Yes,表示同步配置成功。
11. Sharding-JDBC 实现读写分离
11.1. (一)建库建表
Sharding-JDBC 实现读写分离则是根据sql 语句语义分析,当 sql 语句有 insert、update、delete 时,Sharding-JDBC 就把这次操作在主数据库上执行;当 sql 语句有 select 时,就会把这次操作在从数据库上执行,从而实现读写分离过程。
但 Sharding-JDBC 并不会做数据同步,数据同步是配置 MySQL 后由 MySQL 自己完成的。
搭建环境成功后我们在主库和从库上都建库建表:
create database user_db;
use user_db;
create table t_user(
`user_id` bigint(20) primary key,
`username` varchar(100) not null,
`status` varchar(50) not null
);11.2. (二)配置读写分离策略
# 配置数据源,给数据源起别名
# m0为用户数据库
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=m0,s0
# 一个实体类对应两张表,覆盖
spring.main.allow-bean-definition-overriding=true
#user_db 主服务器
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m0.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m0.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m0.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.3.107:3306/user_db?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m0.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m0.password=
#user_db 从服务器
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.s0.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.s0.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.s0.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.3.108:3306/user_db?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.s0.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.s0.password=
# 主库从库逻辑数据源定义 ds0 为 user_db
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.master-slave-rules.ds0.master-data-source-name=m0
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.master-slave-rules.ds0.slave-data-source-names=s0
# 配置user_db数据库里面t_user 专库专表
#spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.actual-data-nodes=m0.t_user
# t_user 分表策略,固定分配至 ds0 的 t_user 真实表
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.actual-data-nodes=ds0.t_user
# 配置主键的生成策略
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.key-generator.column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
# 指定分表策略
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.table-strategy.inline.sharding-column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.table-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=t_user
# 打开 sql 输出日志
spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show=true11.3. (三)测试代码运行
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Test
public void addUser(){
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("Jack");
user.setStatus("Normal");
userMapper.insert(user);
}
@Test
public void findUser() {
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.eq("user_id", 536553906142969857L);
userMapper.selectOne(wrapper);
}12. 什么是 ShardingSphere-Proxy
定位为透明化的数据库代理端,提供封装了数据库二进制协议的服务端版本,用于完成对异构语言的支持。 目前提供 MySQL 和 PostgreSQL 版本,它可以使用任何兼容 MySQL/PostgreSQL 协议的访问客户端(如:MySQL Command Client, MySQL Workbench, Navicat 等)操作数据,对 DBA 更加友好。
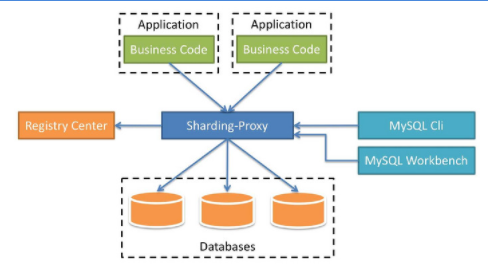
- 向应用程序完全透明,可直接当做 MySQL/PostgreSQL 使用。
- 适用于任何兼容 MySQL/PostgreSQL 协议的的客户端。
- 简单理解为:之前我们要配置多个数据源,而现在我们使用 ShardingSphere-Proxy 之后,我们相当于只操作一个库一个表,而多库多表操作被封装在了 ShardingSphere-Proxy 里面。是一个透明化的代理端。
12.1. (一)下载 ShardingSphere-Proxy
下载地址:
https://archive.apache.org/di...
12.2. (二)Sharding-Proxy 配置(分表)
进入到 conf 中打开server.yaml。
将此部分注释打开即可。
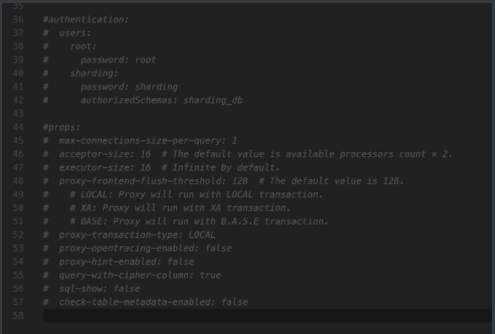
然后我们打开config-sharding.yaml文件进行分库分表的配置
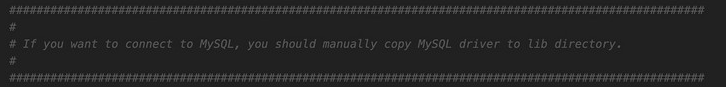
根据提示,如果使用 mysql,需要把 mysql 的驱动 jar 包放到 lib 目录下。拷贝即可。
然后我在主服务器创建了一个数据库
create database test_db;打开如下注释填写对应参数:
schemaName: sharding_db
dataSources:
ds_0:
url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.3.107:3306/test_db?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false
username: root
password: 123456
connectionTimeoutMilliseconds: 30000
idleTimeoutMilliseconds: 60000
maxLifetimeMilliseconds: 1800000
maxPoolSize: 50
shardingRule:
tables:
t_order:
actualDataNodes: ds_${0}.t_order_${0..1}
tableStrategy:
inline:
shardingColumn: order_id
algorithmExpression: t_order_${order_id % 2}
keyGenerator:
type: SNOWFLAKE
column: order_id
bindingTables:
- t_order
defaultDatabaseStrategy:
inline:
shardingColumn: user_id
algorithmExpression: ds_${0}
defaultTableStrategy:
none:然后我们保存进入 bin 目录启动./start.sh。
启动成功后我们进入 logs 目录查看 stdout.log 日志文件。如下图即启动成功!

然后我们进入端口为 3307 的 mysql,ShardingSphere-Proxy默认端口为:3307
mysql -uroot -proot -h127.0.0.1 -P3307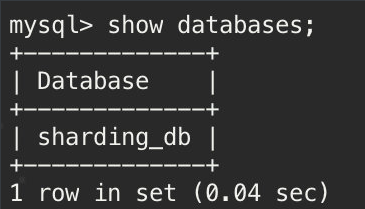
--新建一张表插入条数据。
use sharding_db;
create table if not exists ds_0.t_order(`order_id` bigint primary key,
`user_id` int not null,
`status` varchar(50)
);
insert into t_order(`order_id`,`user_id`,`status`)values(11,1,'jack');
按照 order_id 进行分配,因为是奇数所以被分到了 t_order_1 表里。
12.3. (三)Sharding-Proxy 配置(分库)
我们在主库创建数据库:
create database test_1;我们在从库创建数据库:
create database test_2;我们还是打开config-sharding.yaml进行如下配置:
schemaName: sharding_db
dataSources:
ds_0:
url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.3.107:3306/test_1?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false
username: root
password: 123456
connectionTimeoutMilliseconds: 30000
idleTimeoutMilliseconds: 60000
maxLifetimeMilliseconds: 1800000
maxPoolSize: 50
ds_1:
url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.3.108:3306/test_2?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false
username: root
password: 123456
connectionTimeoutMilliseconds: 30000
idleTimeoutMilliseconds: 60000
maxLifetimeMilliseconds: 1800000
maxPoolSize: 50
shardingRule:
tables:
t_order:
actualDataNodes: ds_${0..1}.t_order_${1..2}
tableStrategy:
inline:
shardingColumn: order_id
algorithmExpression: t_order_${order_id % 2 + 1}
keyGenerator:
type: SNOWFLAKE
column: order_id
bindingTables:
- t_order
defaultDatabaseStrategy:
inline:
shardingColumn: user_id
algorithmExpression: ds_${user_id % 2}
defaultTableStrategy:
none:之后进入 bin 目录下重启一下 Proxy。
./stop.sh
./start.sh进入 mysql
mysql -uroot -proot -h127.0.0.1 -P3307创建表添加数据
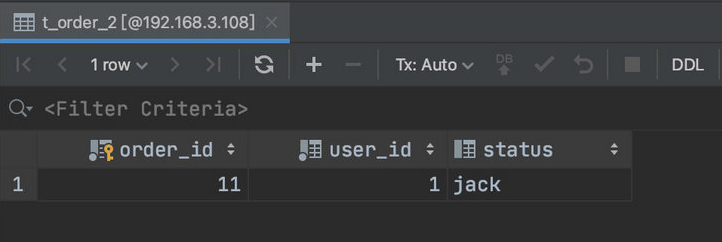
use sharding_db;
create table if not exists ds_0.t_order(`order_id` bigint primary key,`user_id` int not null,`status` varchar(50));
insert into t_order(`order_id`,`user_id`,`status`)values(11,1,'jack');可以看到结果已经插入到了对应的库中表中。
12.4. (四)配置 Sharding-Proxy 读写分离
我们还是使用之前的一主一从搭配主从复制,在主和从上创建数据库:
create database master_slave_user;修改 config-master_slave.yaml 文件(此文件为读写分离的配置)
schemaName: master_slave_db
dataSources:
master_ds:
url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.3.107:3306/master_slave_user?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true
username: root
password: 123456
connectionTimeoutMilliseconds: 30000
idleTimeoutMilliseconds: 60000
maxLifetimeMilliseconds: 1800000
maxPoolSize: 50
slave_ds_0:
url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.3.108:3306/master_slave_user?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true
username: root
password: 123456
connectionTimeoutMilliseconds: 30000
idleTimeoutMilliseconds: 60000
maxLifetimeMilliseconds: 1800000
maxPoolSize: 50
masterSlaveRule:
name: ms_ds
masterDataSourceName: master_ds
slaveDataSourceNames:
- slave_ds_0
# - slave_ds_1之后进入 bin 目录下重启一下 Proxy。
./stop.sh
./start.sh进入 mysql
mysql -uroot -proot -h127.0.0.1 -P3307创建表添加数据
use master_slave_db;
create table if not exists master_slave_user.t_order(`order_id` bigint primary key,`user_id` int not null,`status` varchar(50));
insert into t_order(`order_id`,`user_id`,`status`)values(11,1,'Jack');
此时主库和从库都已经存在数据了。